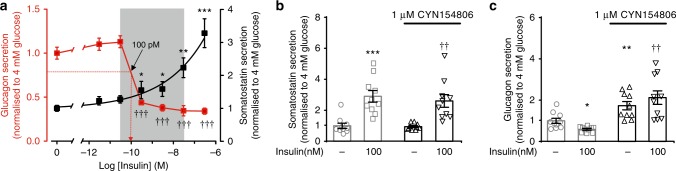
Fig. 2.
Insulin exerts its glucagonostatic effect by somatostatin. a Effects of increasing concentrations of insulin (3 pM, 30 pM, 300 pM, 3 nM, 30 nM, 300 nM; logarithmic abscissa) on glucagon (red) and somatostatin (black) secretion in the presence of 4 mM glucose (n = 10 experiments/6 male mice). Arrow indicates IC50 for inhibitory effect of insulin on glucagon secretion (~100 pM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 and †††p < 0.001 for the effects of insulin on somatostatin and glucagon secretion vs 4 mM glucose alone, respectively, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s post hoc test. b Somatostatin secretion at 4 mM glucose in the absence and presence of insulin and/or CYN154806 (n = 10 experiments//6 male mice). ***p < 0.001 vs 4 mM glucose; ††p < 0.005 vs 4 mM glucose and CYN154806, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s post hoc test. c As in b but glucagon is measured (n = 10 experiments/6 male mice). Secretion has been normalised to secretion rates at 4 mM glucose. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs 4 mM glucose; ††p < 0.005 vs 4 mM glucose and insulin. Data are presented as dot plots of individual experiments and/or mean values ± S.E.M. of all experiments with the experimental series