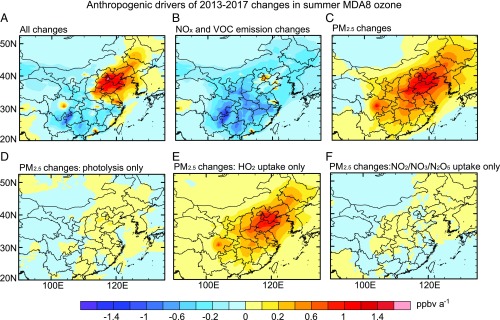
Fig. 4.
Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 changes in mean summertime MDA8 ozone in China. (A–C) GEOS-Chem model results for the changes in MDA8 ozone resulting from: (A) combined effects of 2013–2017 changes in NOx and VOC emissions together with changes in PM2.5, (B) effects of 2013–2017 changes in NOx and VOC emissions alone, and (C) effects of 2013–2017 PM2.5 changes alone including contributions from aerosol chemistry and photolysis rates. (D–F) The different effects of 2013–2017 PM2.5 changes on ozone are separated: (D) radiative effect on photolysis rates, (E) effect of HO2 uptake, and (F) effect of nitrogen oxide (NO2, NO3, and N2O5) uptake.