Fig. 2.
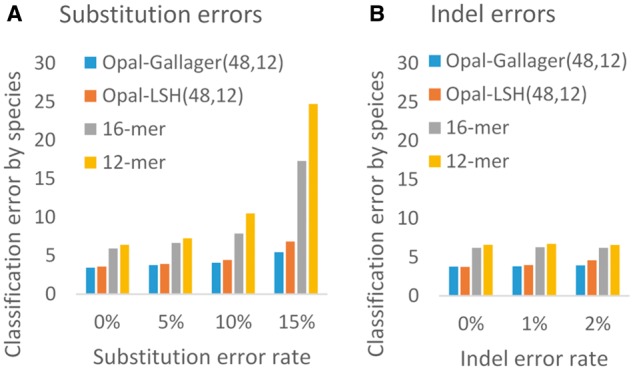
Comparison of Opal against compositional SVM-based approaches. On a synthetic dataset of fragments of length 200 drawn from a dataset of 50 bacterial species (Vervier et al., 2016), using Opal LDPC hash functions (Opal-Gallagher) as features outperforms using the same method with uniformly random LSH functions (Opal-LSH), as well as using contiguous 16- and 12-mers, with (a) substitution errors and (b) indels. We note particularly good robustness against substitution errors
