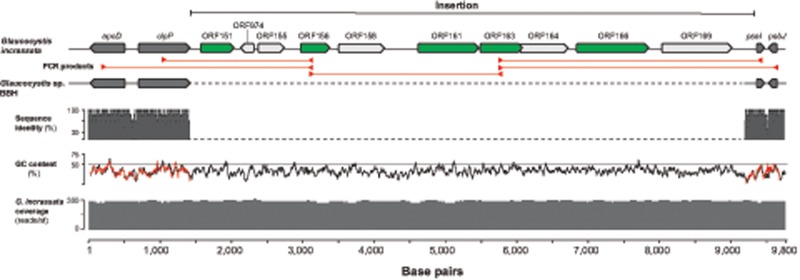
Fig. 3.
—A putative insertion in the plastid genome of Glaucocystis incrassata (SAG 229-2). The 7.9-kb insertion between the typical plastid clpP and psaI genes includes ten ORFs, of which five (highlighted in green) encode putative proteins similar to known bacterial sequences (see text, supplementary figs. S2–S4, Supplementary Material online, for more details). Red arrowheads mark the position of primers designed to amplify flanking regions and fragments of the insertion. The red lines represent the five fragments amplified and sequenced using Sanger sequencing to corroborate contigs generated from Illumina reads. The sequence identity bar graph illustrates the similarity between the homologous regions of Gla. incrassata and Glaucocystis sp. BBH. The GC content percentage of the Gla. incrassata and Glaucocystis sp. BBH sequences is indicated with black and red lines, respectively.