Figure 4. Working model of iVα45 T cells involvement at steady state and during Mm infection.
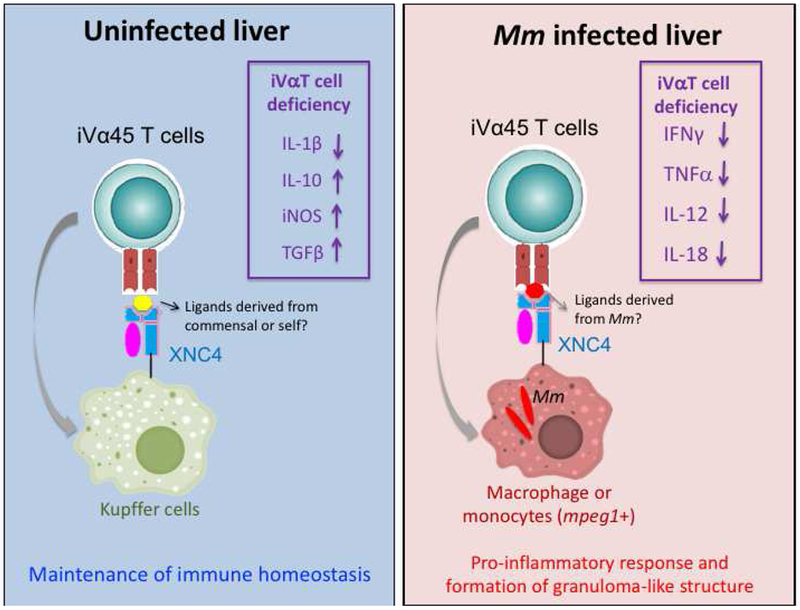
(Left) Putative role of iVα45 T cells in maintaining immune homeostasis is illustrated. The model postulates the interactions of iVα45 T cells with resident leukocytes such as Kupffer cells through the presentation of ligands self or commensal-derived by XNC4. The deregulation of multiple cytokine genes listed resulting from impairing iVα45 T cell function (boxed) is consistent with this model. (Right) Putative role of iVα45 T cells during Mm infection. The model postulates that immune homeostasis is disrupted by the infiltration of Mm-infected monocytes/macrophages presenting Mm-derived ligands in the context of XNC4 that activate iVα45 T cells and induce a pro-inflammatory response. The impaired gene expressions of IFNγ and TNFα as well as IL-12 and IL-18 in iVα45 T-deficient tadpoles (boxed) are consistent with this hypothesis.
