Table 1.
Advantages and limitations of available Next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms.
| Sequencing reaction | Limitation | Advantages | Instruments | Read length in base pairs (bp) | Throughput | Total number of reads | Runtime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sequencing by ligation or SOLiD sequencing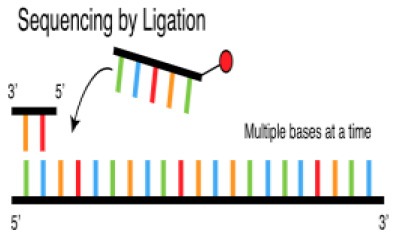
|
This sequencing method has been reported to have problems in sequencing particularly palindromic sequences and relatively slower than other methods. | Relatively cheap | SOLiD 5500 Wildfire | 50 (SES) | 80 Gb | ~700 M+ | 6 days |
| 75 (SES) | 120 Gb | ||||||
| 50 (SES)+ | 160 Gb | ||||||
| SOLiD 5500xl | 50 (SES) | 160 Gb | ~1.4 bn+ | 10 days+ | |||
| 75 (SES) | 240 Gb | ||||||
| 50 (SES)+ | 320 Gb | ||||||
| BGISEQ-500 FCS155* | 50–100 (SES/PES)+ | 8–40 Gb+ | NA† | 24 h | |||
| BGISEQ-500 FCL155 | 50–100 (SES/PES)+ | 40–200 Gb* | NA† | 24 h+ | |||
Sequencing by synthesis:CRT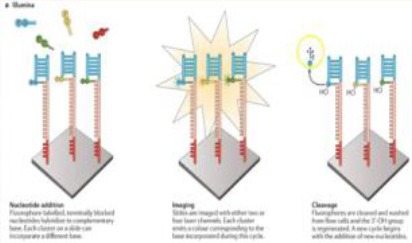
|
Equipment are very expensive. Requires high concentration of DNA. | Potential for high sequencing yield, depending upon sequencer model and desired application | Illumina MiniSeq Mid Output | 150 (SES)+ | 2.1–2.4 Gb+ | 14–16 M+ | 17 h+ |
| Illumina MiniSeq High output | 75 (SES) | 1.6–1.8 Gb | 22–25 M(SES)+ | 7 h | |||
| 75 (PES) | 3.3–3.7 Gb | 44– 50 M(PES)+ | 13 h | ||||
| 150 (PES)+ | 6.6–7.5 Gb+ | 24 h+ | |||||
| Illumina MiSeq v2 | 36 (SES) | 540–610 Mb | 12–15M (SES) | 4 h | |||
| 25 (PES) | 750–850 Mb | 24–30 M (PES)+ | 5.5 h | ||||
| 150 (PES) | 4.5–5.1 Gb | 24 h | |||||
| 250 (PES)* | 7.5–8.5 Gb+ | 39 h | |||||
| Illumina MiSeq v3 | 75 (PES) | 3.3–3.8 Gb | 44–50 M (PES)+ | 21–56 h+ | |||
| 300 (PES)+ | 13.2–15 Gb+ | ||||||
| Illumina NextSeq 500/550 Mid output | 75 (PES) | 16–20 Gb | Up to 260 M (PES)+ | 15 h | |||
| 150 (PES)+ | 32–40 Gb+ | 26 h+ | |||||
| Illumina NextSeq 500/550 High output | 75 (SES) | 25–30 Gb | 400 M(SES)+ | 11 h | |||
| 75 (PES) | 50–60 Gb | 800 M(PES)+ | 18 h | ||||
| 150 (PES)+ | 100–120 Gb+ | 29 h+ | |||||
| Illumina HiSeq2500v2 Rapid run | 36 (SES) | 9–11 Gb | 300 M(SES)+ | 7 h | |||
| 50 (PES) | 25–30 Gb | 600 M(PES)+ | 16 h | ||||
| 100 (PES) | 50–60 Gb | 27 h | |||||
| 150 (PES) | 75–90 Gb | 40 h | |||||
| 250 (PES)+ | 125–150 Gb+ | 60 h+ | |||||
| Illumina HiSeq2500 v3 | 36 (SES) | 47–52 Gb | 1.5 bn (SE) | 2 days | |||
| 50 (PES) | 135–150 Gb | 3 bn(PES)+ | 5.5 days | ||||
| 100 (PES)+ | 270–300 Gb | 11 days+ | |||||
| Illumina HiSeq2500 v4 | 36 (SES) | 64–72 Gb | 2 bbn(SES) | 29 h | |||
| 50 (PES) | 180–200 Gb | 4 B (PES)+ | 2.5 days | ||||
| 100 (PES) | 360–400 Gb | 5 days | |||||
| 125 (PES)+ | 450–500 Gb+ | 6 days | |||||
| Illumina HiSeq 3000/4000 | 50 (SES) | 105–125 Gb | 2.5 bn (SES)+ | 1–3.5 days+ | |||
| 75 (PES) | 325–375 Gb | ||||||
| 150 (PES)+ | 650–750 Gb+ | ||||||
| Illumina HiseqX | 150 (PES)+ | 800–900 Gb per flow cell* | 2.6–3 bn (PES)+ | < 3 days+ | |||
| Qiagen Gene Reader | NA† | 12 genes; 1,250 mutations | NA† | Several days | |||
Sequencing by synthesis: SBS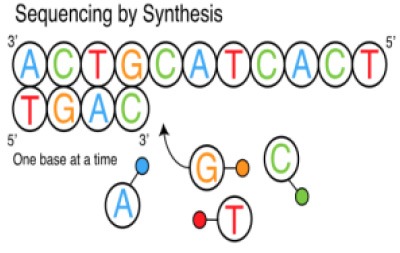
|
Homopolymer errors | Less expensive and relatively fast | 454 GS Junior | Upto 600;400 average (SES,PES)* | 35 Mb+ | ~ 0.1 M+ | 10 h+ |
| 454 GS Junior+ | Upto 1,000;700 average (SES,PES)+ | 70 Mb+ | ~ 0.1 M+ | 18 h+ | |||
| 454GSFLX TitaniumXLR70 | Upto 600;450 mode (SES,PES)+ | 450 Mb+ | ~1 M* | 10 h+ | |||
| 454 GS FLX Titanium XL+ | Up to 1,000; 700 mode (SE, PE)+ | 700 Mb+ | ~1 M+ | 23 h+ | |||
| Ion PGM 314 | 200 (SES) | 30–50 | 400,000– | 23 h | |||
| 400 (SES) | 60–100 Mb+ | 550,000+ | 3.7 h+ | ||||
| Ion PGM 316 | 200 (SES) | 300–500 Mb | 2–3 M+ | 3 h | |||
| 400 (SES)+ | 600 Mb−1 Gb+ | 4.9 h+ | |||||
| Ion PGM 318 | 200 (SES) | 600 Mb−1 Gb | 4–5.5 M+ | 4 h | |||
| 400 (SES)+ | 1–2 Gb+ | 7.3 h+ | |||||
| Ion Proton | Up to 200 (SES) | Up to 10 Gb+ | 60–80 M+ | 2–4 h+ | |||
| Ion S5 520 | 200 (SES) | 600 Mb−1 Gb | 3–5 M+ | 2.5 h | |||
| 400 (SES)+ | 1–2 Gb+ | 4 h+ | |||||
| Ion S5 530 | 200 (SES) | 3–4 Gb | 15–20 M+ | 2.5 h | |||
| 400 (SES)+ | 6–8 Gb+ | 4 h+ | |||||
| Ion S5 540 | 200 (SES)+ | 10–15 Gb+ | 60–80 M+ | 2.5 h+ | |||
Single-moleculereal-time long reads or (PacificBioSciences)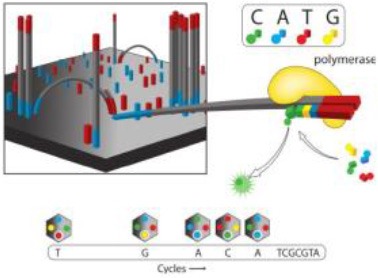
|
Moderate throughput and equipment are very expensive | Fast detection | Pacific BioSciences RSII | ~20 Kb | 500 Mb−1 Gb+ | ~55,000+ | 4 h+ |
| Pacific BioSciences Sequel | 8–12 Kb | 3.5–7 Gb+ | ~350,000+ | 0.5–6 h+ | |||
| Oxford Nanopore MK1MinION | Up to 200 Kb | Up to 1.5 Gb | >100,000 | Up to 48 h | |||
| Oxford Nanopore PromethION | NA† | Upto 4 Tb+ | NA† | NA† |
Manufacturer's data;
Rounded from Field Guide to next-generation DNA sequencers and 2014 update;
Information is not available, as this product has been developed recently.
CRT, Cyclic Reversible Termination; NA, Not Available; PES, Paired End Sequencing; SBS, Sequencing by Synthesis; SES, Single End Sequencing.
