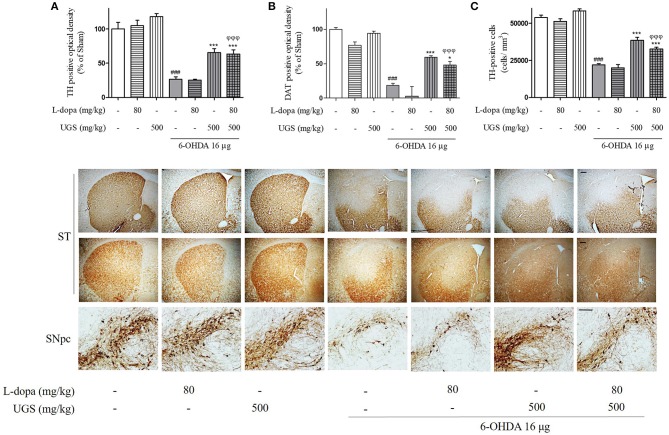
Figure 3.
UGS treated with L-dopa reduced the dopaminergic neuronal damage induced by 6-OHDA in the mouse ST and SNpc. To impede the progress of PD, drugs have to restore dopaminergic neurons against toxicity. To evaluate the restorative effect, dopaminergic neurons were visualized with TH and DAT-immunostaining in nigrostriatal pathway. The optical density of TH and DAT-positive fibers in the ST was measured (A,B). The stereological TH-positive neurons in the SNpc were counted (C). Scale bar = 100 μm. Values of quantification data are given as the mean ± S.E.M. (N = 8). The significance of differences was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's Multiple Comparison Test: ###p < 0.001; mean values were significantly different from the sham group. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001; mean values were significantly different from the 6-OHDA group. ϕϕϕp < 0.001; mean values were significantly different from the 6-OHDA + L-dopa group.