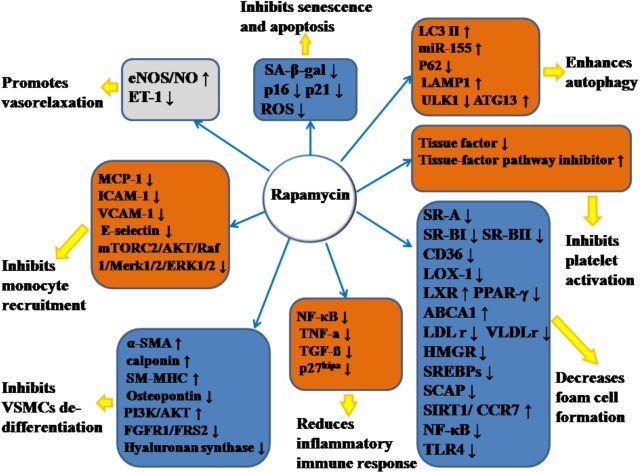
FIGURE 2.
Anti-atherosclerotic effects of rapamycin and its molecular targets. Rapamycin inhibits the formation and development of atherosclerosis (AS) by promoting vasorelaxation, inhibiting monocyte recruitment, inhibiting VSMCs de-differentiation, reducing inflammatory immune response, decreasing foam cell formation, inhibiting platelet activation, enhancing autophagy, and inhibiting senescence and apoptosis. The notation ↑ indicates increase or activation, and ↓indicates decrease or suppression. LOX-1, lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein-1; SR-A, scavenger receptor, class A; SR-BI, scavenger receptor, class B, type I; SR-BII, scavenger receptor, class B, type II; LAMP1, lysosome-associated membrane protein 1; LC3, light chain 3; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; ET-1, endothelin-1; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; LXRa, liver-X-receptor alpha; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SM-MHC, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain; FGFR1, fibroblast growth factor receptor-1; FRS2, fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2; SA-β-gal, senescence-associated galactosidase; ATG13, autophagy-related protein-13; LDLr, low-density lipoprotein receptor; VLDLr, very low-density lipoprotein receptors; HMGR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; SREBPs, sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; SCAP, SREBP cleavage-activating protein; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; miR-155, microRNA-155; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; ULK1, Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; CCR7, C-C chemokine receptor type 7; CD36, cluster of differentiation; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; mTORC2, mTOR complex 2.