Fig. 6.
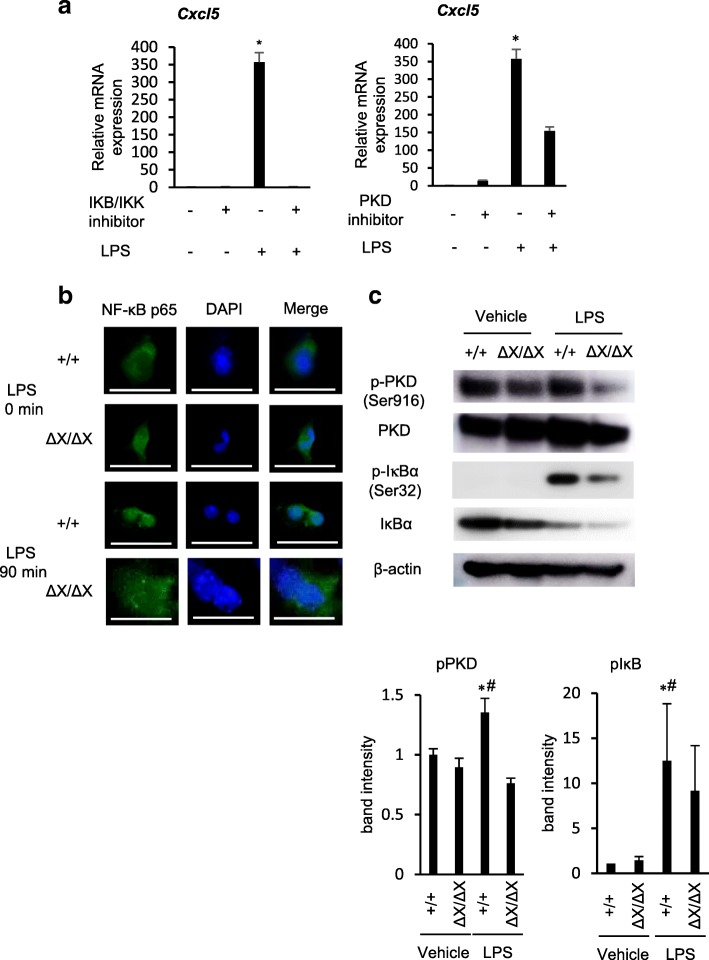
Role of PLCε in LPS-induced NF-κB activation. a Primary-cultured AECs from PLCε+/+ mice were treated with and without the IKB/IKK inhibitor (20 μM) or the PKD inhibitor (10 μg/ml) 0.5 h and 1 h before administration of LPS (500 ng/mL) or vehicle for 16 h. Expression of the Cxcl5 gene was analyzed by using qRT-PCR (n = 7/group). Values represent p-values between LPS-stimulated AECs and LPS-stimulated AECs with the IKB/IKK inhibitor or the PKD inhibitor. *, p < 0.05. b Primary cultured AECs from PLCε+/+ and PLCε∆X/∆X mice were subjected to NF-κB p65 (green) immunostaining after stimulation for 90 min with LPS (500 ng/ml) (n = 8 mice/group). The anti-NF-κB p65 antibody (1:50) was used. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 25 μm. c Proteins, prepared from the primary cultures of PLCε+/+ and PLCε∆X/∆X lung AECs in 1.5 h after treatment with LPS (500 ng/ml) or vehicle (n = 8 mice/group) were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (upper panel). The intensity of each phospho-protein band was divided by the intensity of each total protein band. The average intensities obtained from at least three independent experiments were shown as the mean ± S. D with p-values (lower panels). *, p < 0.05 between control and LPS administration, #, p < 0.05 between PLCε genotypes