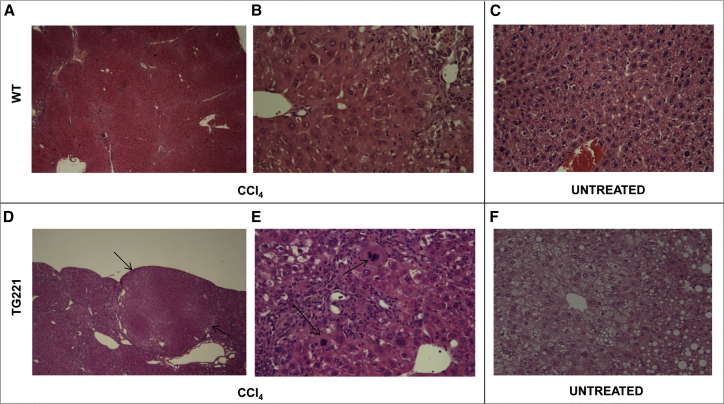
Figure 3.
CCl4-Treated TG221 Mice Present Neoplastic Proliferative Lesions
H&E-stained livers from untreated and CCl4-treated mice (200× and 40× magnification). In WT mice (A–C), alterations in the lobular structure of the liver and hepatic degeneration, with the presence of regenerative nodules typical of hepatic cirrhosis, were detected in CCl4-treated animals (A and B), but not in untreated mice (C). In TG221 mice (D–F), the same structural alterations in WT animals were observed in CCl4-treated animals (D and E), with a higher and more intense grade of inflammation. In addition, proliferative tumor lesions were present (black arrows, D) and associated with dysplastic aspects and atypical mitosis (black arrows, E), resembling hepatocellular carcinomas. (F) These alterations were absent in livers from untreated TG221 mice, albeit steatohepatitis changes, typical of the TG221 mouse,16 were observed.