Figure 1.
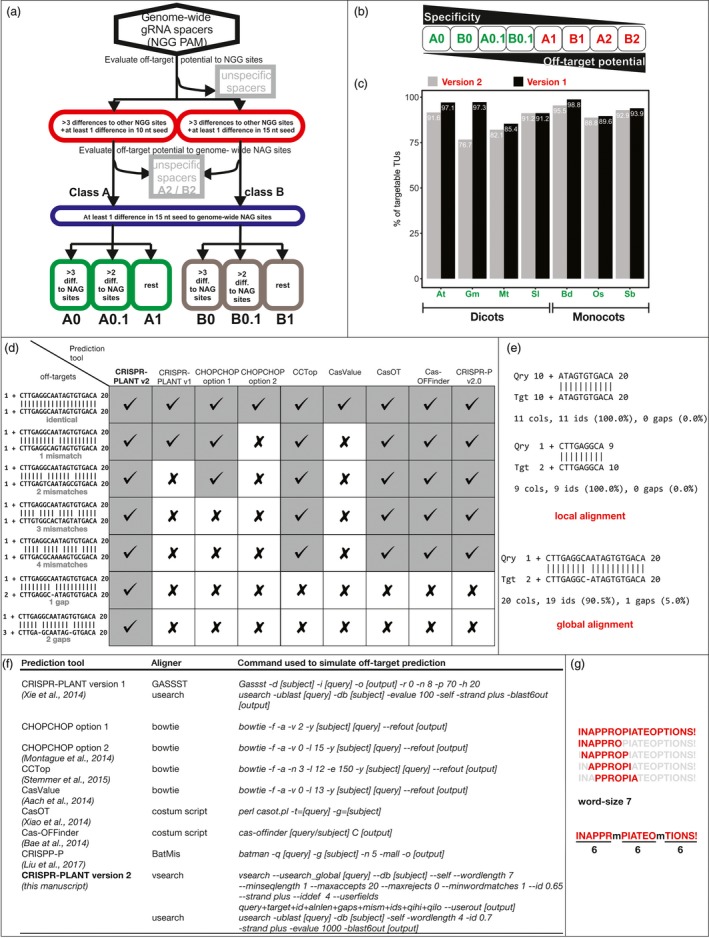
An improved off‐target analysis resulted in genome‐wide prediction of highly specific CRISPR/Cas9 spacer sequences for seven plant genomes. (a) Pipeline used to detect off‐targets and to classify spacer sequences. (b) Classes for spacers ordered by specificity and off‐target potential. (c) Comparison of highly specific targetable transcription units between the new CRISPR‐PLANT v2 and the old v1. (d) Seven different off‐target prediction tools were tested for their ability to find seven different potential off‐target sequences in an artificial rice chromosome 1 sequence. Checks indicate successful alignment and detection while crosses indicate a failure. (e) Examples of local and global alignment between a target sequence and an off‐target sequence with a one base pair deletion. (f) Exact programs, command and options used in the comparison of off‐target tools. (g) Example of words created by the word‐size seven, which is insufficient to detect sequences with two mismatches that are equally spaced out. At: Arabidopsis thaliana; Gm: Glycine max; Mt: Medicago truncatula; Sl: Solanum lycopersicum; Bd: Brachypodium distachyon; Os: Oryza sativa; Sb: Sorghum bicolor.
