Figure 6.
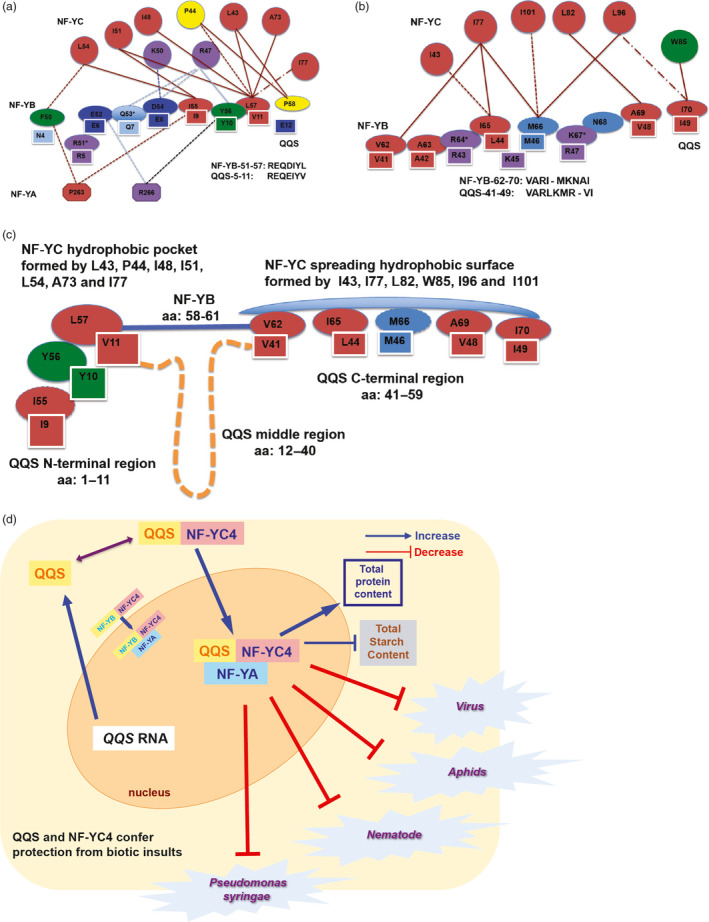
QQS binding sites with NF‐YC and speculated model for QQS and NF‐YC4‐induced changes in composition and plant defense. (a) Model of the interactions of NF‐YB‐51‐57, NF‐YC, and NF‐YA, and the QQS‐5‐11 interactions with NF‐YC. (b) Model of the interactions of NF‐YB‐62‐70 and NF‐YC, and the QQS‐41‐49 interactions with NF‐YC. NF‐YB‐62‐70 are not in contact with NF‐YA, so NF‐YA is not represented here. See Figure S6a,b for detailed explanation of the models, which are based on analysis of previously published crystal structure data [Protein Database Bank (PDB) IDs: 1N1J (Romier et al., 2003) and 4 AWL (Nardini et al., 2013)]. (c) QQS binds to two NF‐YC hydrophobic interfaces. Based on the sequence similarity between QQS‐5‐11 and QQS‐41‐49 and the NF‐YB N‐terminal region, we propose QQS binds to two NF‐YC hydrophobic interfaces that the NF‐YB N‐terminal region binds to (Figure 6a,b). However, NF‐YB only has three residues (aa from 58 to 61, solid light blue line) in α1 to link the two binding sites and QQS has a 29‐residue long fragment (aa 12–40, dashed yellow line) to link the QQS N‐ and C‐terminal binding sites. Shape of the residues: octagon, NF‐YA; ellipse, NF‐YB; circle, NF‐NC; and shaded rectangle, QQS. Colour of residues represents the polarity and hydrophobicity: red, aliphatic; purple, negatively charged; blue, positively charged; light blue, polar; green, aromatic; and yellow, unique Pro (P). The distance cut‐offs for interaction: 5 Å for hydrophobic interaction, 6 Å for ionic interaction and cation‐pi interaction, and 3.5 Å and 4.0 Å for hydrogen bond when the donor is oxygen/nitrogen and sulphur, respectively. Solid line represents the interaction in both 1N1J and 4 AWL, the broken line in 1N1J only, and the dashed line in 4 AWL only. The colour of the lines represents the type of interaction: dark red, hydrophobic interaction; light blue, hydrogen bond; dark blue, ionic interaction; and black, cation‐pi interaction. The residue marked with * is in contact with DNA within 5 Å. (d) Proposed model of defense priming by QQS: QQS/NF‐YC4 protein complex moves to the nucleus, binding NF‐YA to regulate transcription of downstream genes. QQS may compete with NF‐YB to bind NF‐YC, thus altering the NF‐Y protein complex.
