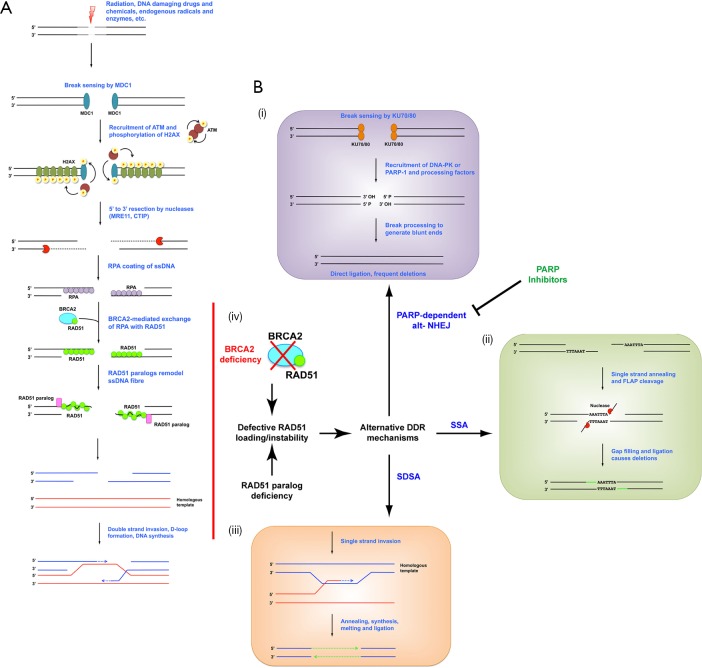
Figure 1.
DSBR pathways and the effect of RAD51 paralog loss on pathway choice. (A) Schematic of homologous recombination. Double strand breaks are detected by the sensor protein MDC1, which recruits the ATM dimer. ATM autophosphorylates, becomes a monomer and then phosphorylates H2A.X, which serves as a recruitment signal for additional complexes including exonucleases. Exonucleases resect the broken ends in a 5' to 3' direction to generate 3' overhanging ssDNA fibres, which are then coated with RPA. BRCA2 loads RAD51 onto the fibres by exchanging it with RPA. The RAD51-ssDNA fibres are remodelled and stabilized by RAD51 paralogs, and filaments are engaged in homology searching the genome. RAD51 catalyses the annealing of the ssDNA fibres to their homologous template for resynthesis. The junction structure is then resolved and ligated to generate intact duplex. (B) Schematic of alternative DSBR mechanisms: (i) alt-NHEJ. Binding of the KU70/80 heterodimer to the break recruits DNA-PK or PARP-1 and their associated end processing factors. Once 3' hydroxyl and 5' phosphate termini are restored ends are blunt-ligated; (ii) SSA. Regions of microhomology between ssDNA fibres are annealed, generating 3' overhanging flaps. These are cleaved by structure-specific endonucleases and the remaining gaps are filled and ligated; (iii) SDSA. Single strand invasion occurs as in HR, but only one end of a break aligns with a homologous template for polymerase extension. The newly synthesized DNA is then melted from its template and annealed to the existing 3' ssDNA overhang on the other break end; (iv) effect of RAD51 loading defects on pathway choice. RAD51 paralog or BRCA2 deficiency lead to instability or loss of RAD51 ssDNA fibres. Without RAD51 fibres HR cannot be completed and alternative error prone repair mechanisms are engaged. In these circumstances PARP-dependent alt-NHEJ is a critical repair mechanism. Chemical inhibition of PARP causes an overuse of classical DNA-PK driven NHEJ with subsequent cytotoxic deletions and chromosome structural aberrations. NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA; SSBR, single strand break repair; DSBR, double strand break repair; RPA, replication protein A; SSA, single strand annealing; SDSA, synthesis dependent strand annealing; HR, homologous recombination; DDR, DNA damage repair.