Figure 4.
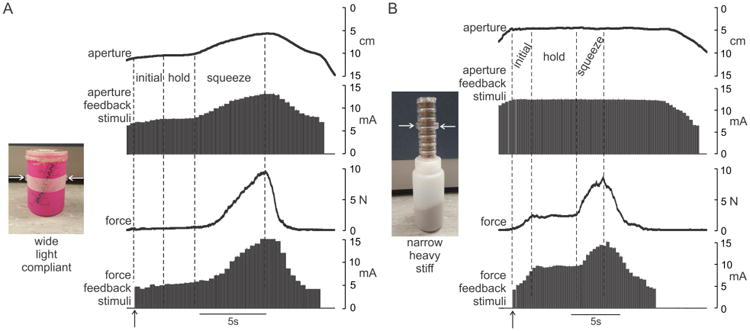
Example sensor and feedback signals during grasping of two objects: (A) wide, lightweight, and compliant object and (B) narrow, heavy, and stiff object. Horizontal arrows on images indicate contact points on small disks fixed to objects. Each grasp was divided into three phases, an initial phase during which grip force increased to lift and support the weight of the object, a steady hold phase, and a squeeze phase during which additional grip force was applied to the object to aid in identifying object compliance. Note that vertical axes of aperture signals are inverted (i.e. small apertures towards the top) to allow more ready comparison to feedback signals. Vertical arrows indicate time at which grip force exceeded minimum threshold and force feedback was initiated.
