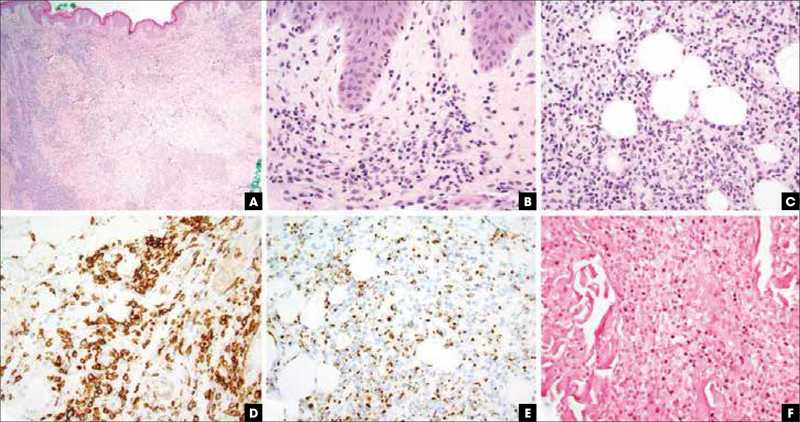
FIGURE 2.
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, pathologic features. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 20x, leukemic appearing multinodular, perivascular, and periadnexal mononuclear cell infiltrate. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400x, vacuolar interface alteration at the dermoepidermal junction and extravasated erythrocytes admixed with perivascular NK and/or T cells, evidencing cytotoxic damage. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400x, lobular panniculitic infiltrates. (D) CD56 immunohistochemistry highlights the atypical NK cells. (E) Granzyme B immunohistochemistry is diffusely positive. (F) Epstein–Barr virus encoded RNA in situ hybridization study revealing nuclear virus positivity in many of the atypical cells. NK, natural killer.