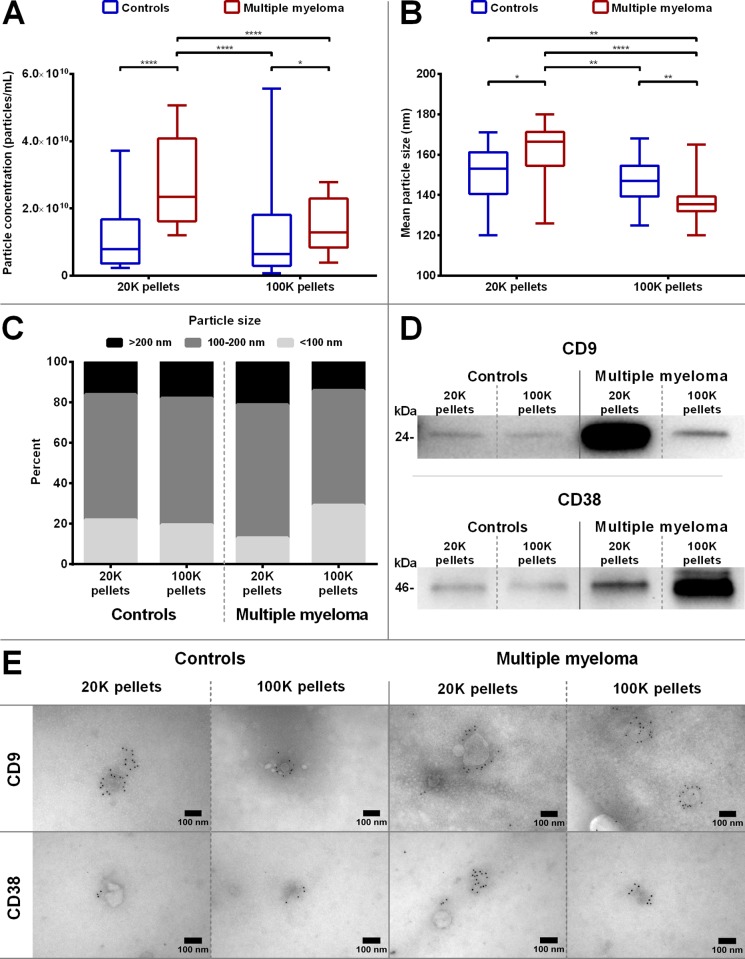
Fig 1. Analysis of EV characteristics.
Nanoparticle tracking analysis was performed on each pellet (20K and 100K) for controls and MM patients to determine A) particle concentrations and B) mean particle size. The boxplots depict the median, the 25 and 75 percentiles and the whiskers min to max. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001. C) The distribution of particle sizes was grouped into three subgroups (<100 nm, 100–200 nm, and >200 nm). D) The pellet pools were analysed by Western blotting for EV-marker CD9 and ectoenzyme CD38. Equivalent volumes of each pellet pool (20K and 100K) from both controls and MM were loaded on the gels. As expected, tetraspanin CD9 was present in all pellet types but enriched in MM pellets, especially in the 20K pellet pool. CD38 was found in all pellet pools, but most abundant in MM pellets (mostly in the 100K pellet pool). E) Immunoelectron microscopy images of gold immunolabelled CD9+ and CD38+ EVs in pellet pools of control and MM pellets (20K and 100K pellets). Images include scale bars determined with ImageJ software.