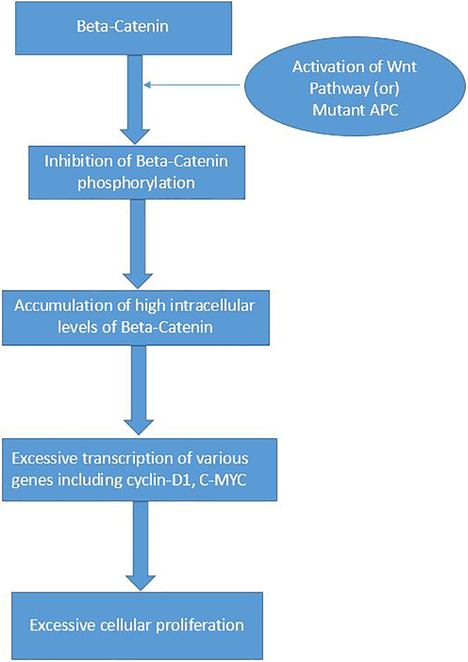
Fig. 10 -.
The Wnt-Beta-Catenin pathway in Desmoid Fibromatosis
β-catenin molecule is normally located in the adherens junctions. Adenomatosis Polyposis Coli (APC) gene complex regulates the phosphorylation of β-catenin and its subsequent degradation in the proteasomes. When there is activation of Wnt (by its binding with its ligand) or there is mutation in the APC gene, it prevents the APC induced phosphorylation of the β-catenin. This results in excessive intracellular accumulation of β-catenin, which translocates to the nucleus and causes significant activation and transcription of various genes including Cyclin-D1 and C-MYC. In turn, this leads to a cascade of events resulting in excessive cell proliferation.