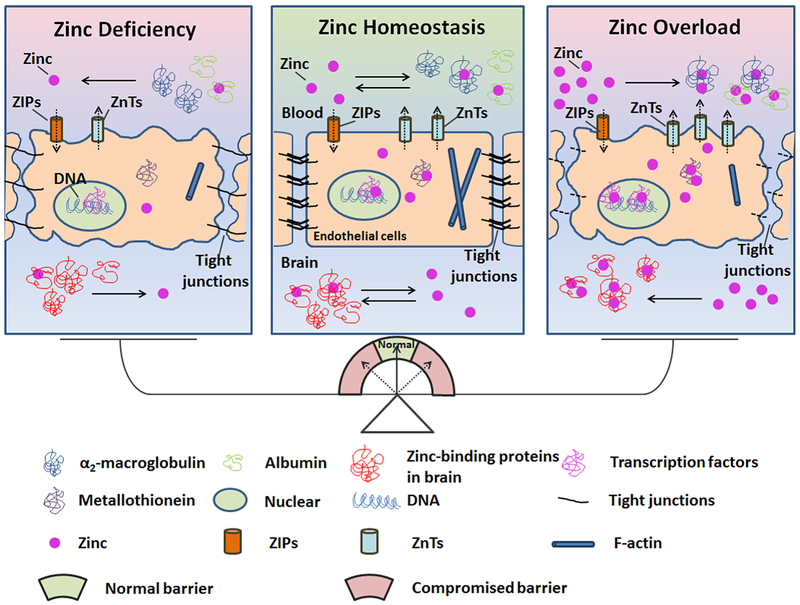
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the role of zinc homeostasis in the normal function of the BBB. Most zinc is found in zinc containing proteins, regulating protein-DNA, protein-RNA, and protein-protein interactions. Most plasma zinc is in binding with albumin and α2-macroglobulin, which serve as a zinc pool in circulation. The BBB separates the plasma zinc from the brain under physiological conditions. The ZIP and ZnTs families have been identified to regulate zinc concentration and keep zinc homeostasis in endothelial cells. The ZIP family increases cytoplasmic zinc by increasing zinc uptake, thereby decreasing plasma zinc and prompting zinc release. The ZnTs family reduces cytoplasmic zinc by exporting cellular zinc, which increases plasma zinc concentrations and helps the movement of cytoplasmic zinc into intracellular organelles. ZnTs are more easily inducible and sensitive to changes in concentration of zinc than ZIPs. Pathological insults, such as cerebral ischemia, break the zinc homeostasis and result in BBB disruption. The compromised BBB, which could not block plasma zinc into brain tissue, deteriorates the dyshomeostasis of zinc.