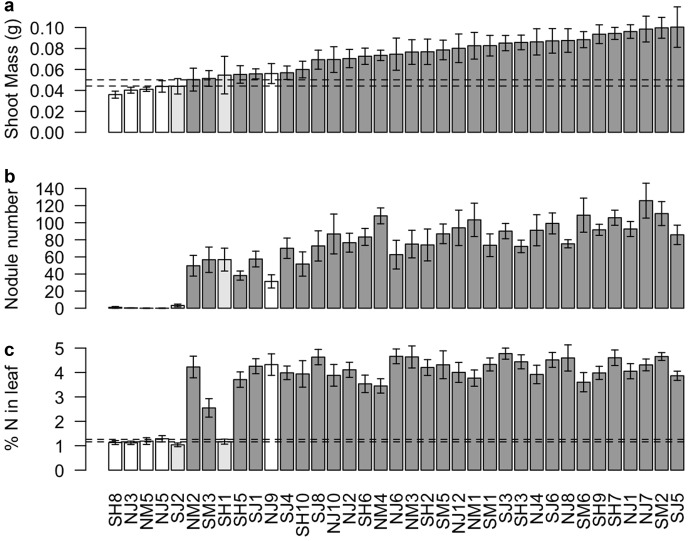
Fig. 1.
Abundant variation in cooperation among closely related strains of Mesorhizobium. Shown are shoot biomass (a), root nodule number (b), and percent of leaf tissue comprised of nitrogen (c) for the host plant, Acmispon wrangelianus, when inoculated with different strains. Bars indicate mean Mesorhizobium genotype effects averaged across three coevolved, inbred plant lines (n = 234 pots). Genomic analysis reveals three categories of strains: strains that lack the symbiosis island (white), strains that contain an intermediate number of symbiosis genes (light gray), and strains that contain nearly all symbiosis genes as well as the full symbiosis island (dark gray). Error bars indicate standard error. Dashed lines indicate standard error around the means for Mesorhizobium-free plants. Mesorhizobium-free plants did not form nodules