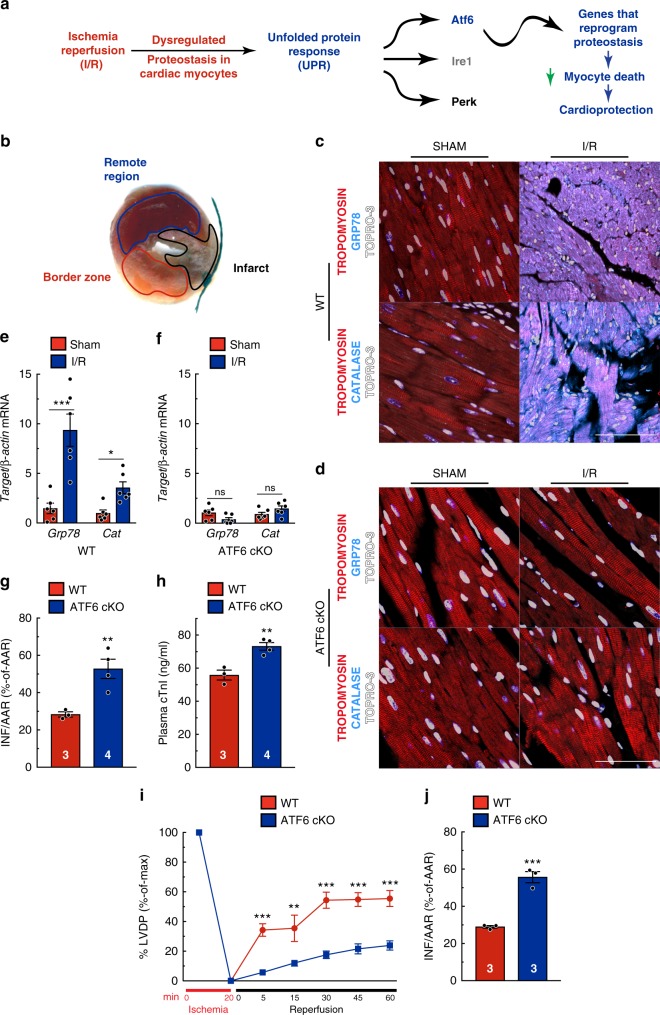
Fig. 1.
ATF6 in cardiac myocytes protects the heart from I/R injury. a Diagram of the hypothetical activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) by ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in the heart. b Post AMI cross-section of the left ventricle of a mouse heart after I/R and TTC staining to identify the infarct region (black), border zone (red) CAT (cyan), tropomyosin (red), and nuclei (TOPRO-3, white) in the border zone of wild-type (WT) (c) or ATF6 cKO (d) hearts subjected to either sham or I/R surgery with 24 hours of reperfusion. Tissue sections are representative images from one mouse per condition. Scale bar represents 50 µm. e, f Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) for Grp78 or Cat in sham or border zone of post-I/R hearts in WT (n = 6) (e), ATF6 cKO (n = 6) (f). g, h Infarct sizes (h) and plasma cardiac troponin I (cTnI) (i) in WT (n = 3) and ATF6 cKO (n = 4) mice post I/R. i, j Left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP) (i) and relative infarct sizes (j) post ex vivo I/R (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Two-group comparisons were performed using Student’s two-tailed t test, and all multiple group comparisons were performed using a one-way ANOVA with a Newman–Keuls post hoc analysis. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001; ns not significant