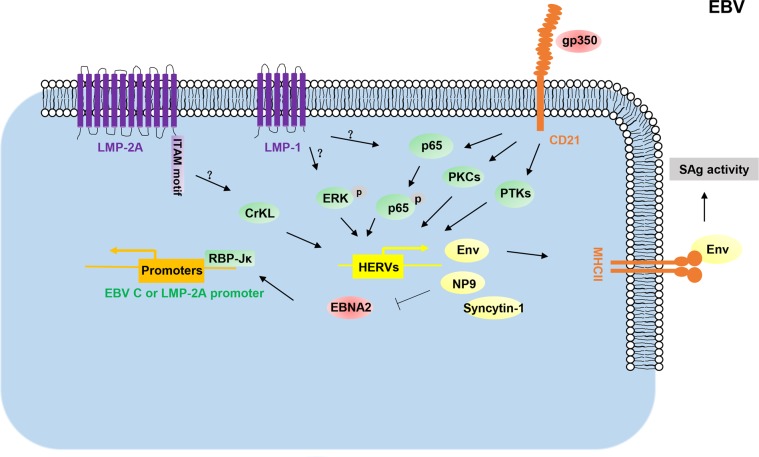
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of potential mechanisms for EBV promoting HERV transactivation.
EBV infection can activate HERV expression through its gp350 protein interaction with its cellular receptor CD21 in the resting B-lymphocytes and PBMC. In infected B-lymphocytes, viral LAM-2A and LMP-1 activate the expression of HERV-K as superantigens (SAgs) to activate T-cell-mediated SAgs immune response. HERV-K Np9 binds to EBNA2 and negatively affects the EBNA2-mediated activation of the viral C- and LMP2A promoters. LAM-2A: Latent membrane proteins 2A; ITAM motif: an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; LMP-2A: LMP-1 latent membrane proteins 1; EBNA2: viral nuclear antigen 2; gp350: glycoprotein 350