Figure 4. Oligomerisation of BAK restricts its ubiquitination and induces Parkin activity.
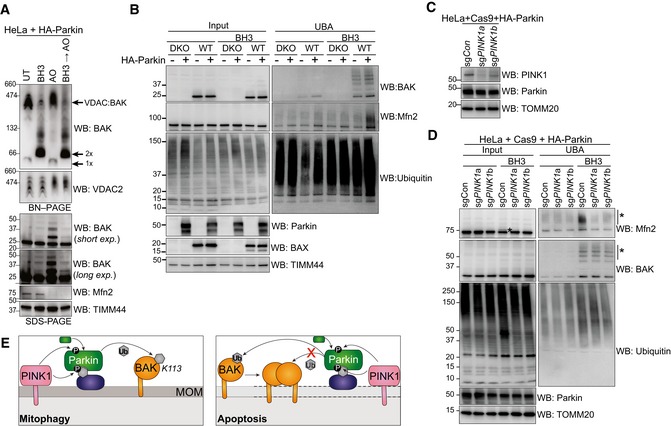
- BN–PAGE and SDS–PAGE of HeLa + HA‐Parkin cells treated with 1 μM of each of ABT‐737 and S63485 for 3 h (BH3), antimycin A and oligomycin (AO) for 2 h or a combination of the two. Experiment was performed in the presence of 10 μM QVD.oph and immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments.
- UBA enrichment of ubiquitinated proteins from HeLa + HA‐Parkin cells, BAX −/− BAK −/− (DKO) HeLa cells or wild‐type (WT) HeLa cells expressing HA‐Parkin in response to 1 μM of each of ABT‐737 and S63485 for 3 h (BH3) in the presence of QVD.oph (10 μM). Representative of three independent experiments.
- HeLa cells expressing HA‐Parkin and Cas9 were transduced with sgRNA targeting PINK1 or a non‐targeting sgRNA control, treated with AO (2 h) to stabilise PINK1 expression and immunoblotted for PINK1.
- Parkin activity induced by apoptotic mitochondrial damage is PINK1‐dependent. UBA enrichment of ubiquitinated proteins from HeLa cells generated in (C) in response to 1 μM of each of ABT‐737 and S63485 for 3 h (BH3) in the presence of QVD.oph (10 μM). (*) ubiquitinated protein. Representative of two independent experiments.
- Schematic showing Parkin ubiquitination of BAK monomer in non‐apoptotic cells, but not the BAK homo‐dimer in cells undergoing apoptosis. In response to mitophagy stimuli, PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin to recruit Parkin, which in turn is phosphorylated by PINK1 to become activated to ubiquitinate monomeric BAK on K113. Mitochondrial outer membrane (MOM) permeabilisation driven by BAK oligomers during apoptosis provokes Parkin activity in a PINK1‐dependent manner. Although Parkin can ubiquitinate mitochondrial outer membrane substrates (e.g. Mfn2) to promote mitochondrial clearance, it cannot ubiquitinate dimerised BAK on K113.
Source data are available online for this figure.
