Figure EV1. Synthesis and characterization of CCB02.
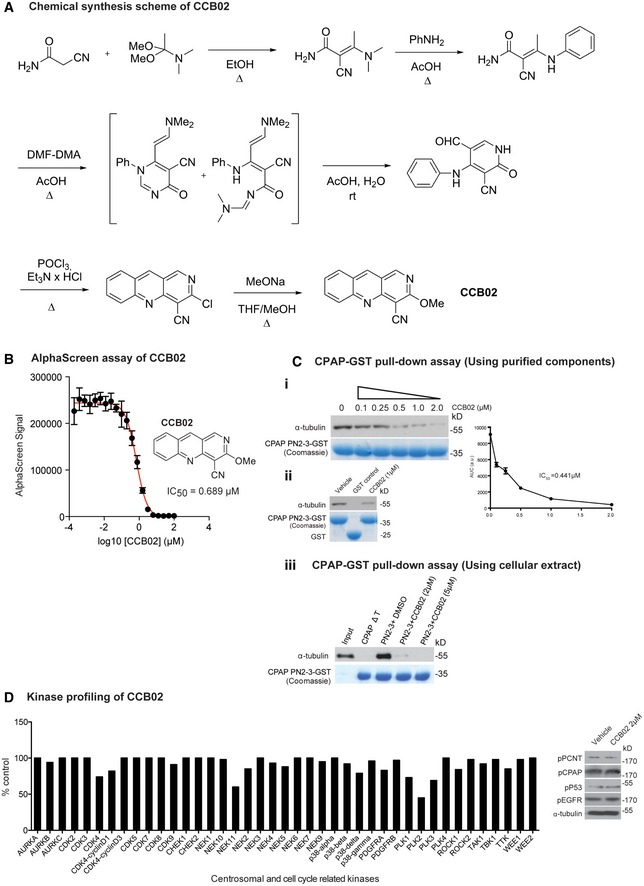
- Chemical synthesis of CCB02.
- CCB02 the derivative of HTS1 exhibits a dose‐dependent reduction of CPAP‐tubulin AlphaScreen signal. Error bars indicate data from a triplicate determination.
- CPAP‐GST pull‐down assay to support the findings of AlphaScreen assay. This CPAP‐GST pull‐down assay uses purified components of CPAP PN2‐3 and tubulin. Semi‐quantitative Western blot shows that CCB02 perturbs CPAP PN2‐3–tubulin interaction in a dose‐dependent manner with an approximately estimated IC50 value of 0.441 μM. The bait protein GST‐tagged PN2‐3 domain of CPAP is shown in Coomassie (bottom panel). The results derived from at least three independent experiments for intensity calculations (i). CPAP PN2‐3‐GST but not GST alone interacts with tubulin. CCB02 (1 μM) perturbs CPAP PN2‐3–tubulin interaction. Purified GST‐tagged PN2‐3 domains of CPAP and GST are shown in Coomassie (bottom panel) (ii). Similar CPAP‐GST pull‐down assay using cell extracts to show CCB02 prevents cellular tubulin binding to GST‐tagged PN2‐3 domain of CPAP. CCB02 at 2 and 5 μM (top panel Western blot) prevents binding of cellular tubulin to PN2‐3 (iii). We used CPAPΔT, a variant that will not interact with tubulin as a negative control. Addition of DMSO instead of CCB02 is a positive control.
- To evaluate the specificity, CCB02 was profiled against a broad panel of human protein kinases, including cancer‐relevant mutant kinases. Of the 469 kinases tested, CCB02 showed no significant inhibitory activity against family of centrosomal and other cell cycle‐related kinases even at higher concentration of CCB02 (5 μM). Note that our cell‐based experiments used concentration ranging from 1 to 2 μM. Experimental values are average of three independent experiments. (N) = 3. The kinases that represent < 10% of inhibitory activity compared to control are considered significant. Based on this, CCB02 does not seem to affect the activity of centrosomal and cell cycle‐related kinases. The complete result of in vitro kinases profiling is given in Table EV2 in the article. Western blot at right panel: Cell extracts treated with 2 μM of CCB02 were analyzed for phosphorylated substrates such as p‐PCNT, p‐CPAP, p‐P53, and p‐EGFR that are phosphorylated by PLK1, Aurora A, CDK2 (other like, CHK1 or CHK2 or ATM or ATR) and EGFR, respectively. Treatment with CCB02 does not alter the phosphorylation status of these proteins, indicating that the mechanism of CCB02 is not through inhibiting any of these cell cycle‐ or centrosome‐related kinase activities.
