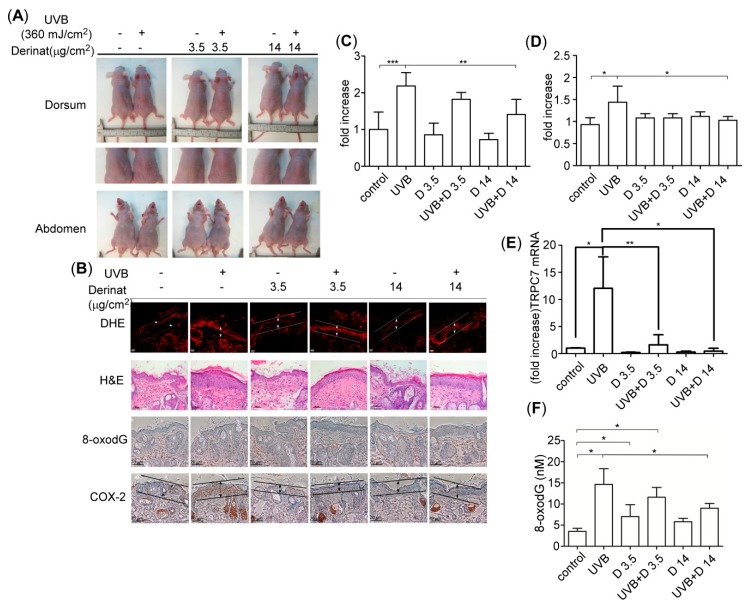
Figure 7.
The effect of Derinat on UVB induced skin damage in BALB/c-nu mice. (A) BALB/c-nu mice were covered with Derinat hydrogel or pure hydrogel for 3 h and then irradiated with 360 mJ/cm2 UVB. After seven days, the images of animals presented UVB-induced desquamation in the dorsal areas but no effect on the abdominal areas. The middle panel shows the amplified images from the dorsal areas of UVB-induced desquamation; (B) Derinat protected BALB/c-nu mice skin from UVB-induced epidermal proliferation, DNA damage and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression. The skins of normal and UVB irradiated mice covered with Derinat hydrogel or hydrogel were stained with DHE and H & E (hematoxylin and eosin), and the oxidative DNA damage 8-oxodG was analyzed via an immunohistochemical assay with a specific anti-8-oxodG mouse monoclonal antibody. The expression of COX-2 in the epidermis was detected with an anti-COX-2 rabbit monoclonal antibody; (C,D), the quantification of intracellular ROS production and COX-2 level from (B) shown in arroew indicated region includes both epidermis and dermis without sebaceous glands (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). Derinat decreased the UVB-induced level of TRPC7 (E) and DNA damage 8-oxodG (F) in BALB/c-nu mouse skin based on qRT–PCR and ELISA assay, respectively (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).