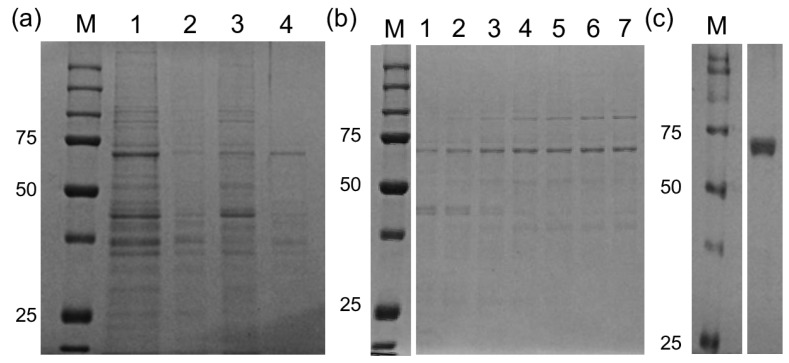
Figure 3.
Purification of TGR from M. vogae tetrathyridium larvae. (a) Ammonium sulfate precipitation of a total aqueous extract from tetrathyridium larvae was carried out in three steps (0%–25%, 25%–50% and 50%–85% ammonium sulfate saturation) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions (lane 1 corresponds to the total extract, lanes 2, 3 and 4 to 0%–25%, 25%–50% and 50%–85% ammonium sulfate saturation fractions, respectively); (b) The 25%–50% ammonium sulfate saturation fraction was further purified by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) on a 16/600 Superdex 200 column; lanes 1 to 7 show fractions were the TR and GR activities eluted; (c) SEC fractions containing TR and GR activities were pooled and subjected to a anionic chromatography on a MonoQ column. Bound proteins were eluted using a NaCl 10–1000 mM gradient and the fractions obtained were analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. The lane shown corresponds to the fraction with maximal TR and GR activity, which eluted at NaCl 300 mM. The gels shown in (a,b) were coomassie stained and the gel shown in (c) was silver stained. M denotes molecular weight markers.