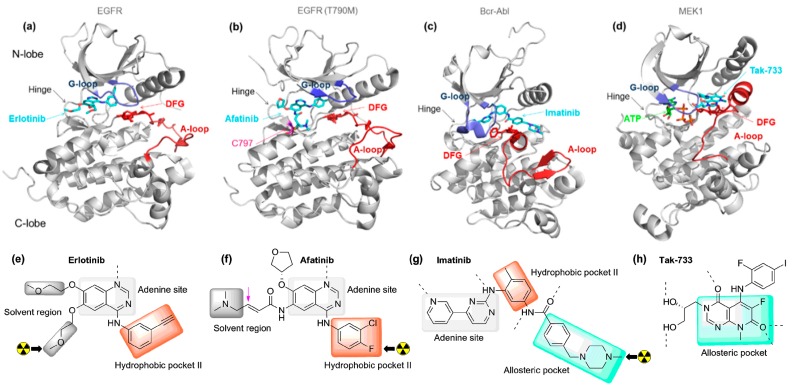
Figure 1.
Representative examples of the primary types of small molecule kinase inhibitors including a DFG-in irreversible inhibitor. Kinases are shown in grey, the activation loops in burgundy, the glycine-rich loops in blue and the DFG motif in red (sticks). The carbon atoms of the inhibitors and the ATP are respectively represented in cyan and green (a–c); The chemical structures and schematic binding modes of the inhibitors are depicted. For inhibitors that have been radiolabeled for PET imaging, the position of the radionuclide (carbon-11 and fluorine-18) is indicated with a black arrow (e–g); (a,e) Type I inhibitor; co-crystal structure of erlotinib bound to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (DFG-in) (PDB ID: 1M17); (b,f) Type I inhibitor (irreversible); co-crystal structure of Afatinib bound to EGFR T790M (DFG-in) (PDB ID: 4G5P); (c,g) Type II inhibitor; co-crystal structure of imatinib bound to Bcr-Abl (DFG-out) (PDB ID: 1IEP); (d,h) Type III inhibitor; co-crystal structure of Tak-733 bound to MEK1 (DFG-in) (PDB ID: 3PP1).