Table 2.
The main classes of non-flavonoid polyphenols with chemical structure, representative members and dietary sources [36,39,45].
| Class of Non-Flavonoids | Chemical Structure | Representative Members | Dietary Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids—Benzoic acids/hydroxybenzoates C6–C1 | 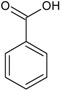 |
Gallic acid p-hydroxy-benzoic Syringic acid Vanillic acid | Clove buds (Eugenia caryophyllata) Grains: wheat (Triticum vulgare), rice (Oryza sativa), oat (Avena sativa), rye (Secale cereale), barley (Hordeum vulgare) Dates (Phoenix dactylifera) |
| Phenolic acids—Cinnamic acids/hydroxycinnamates C6–C3 | 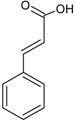 |
p-coumaric acid Caffeic acid Ferulic acid Chlorogenic acid | Apples (Malus domestica) Dates (Phoenix dactylifera) Green coffee beans (Coffea arabica) Carrots (Daucus carota) |
| Stilbenes C6–C2–C6 | 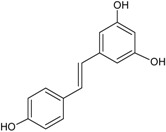 |
Resveratrol | Red wine, peanuts (Arachis hypogaea), red cabbage (Brassica olearaceae Capitata Group), spinach (Spinacia oleracea) |
| Other polyphenols | 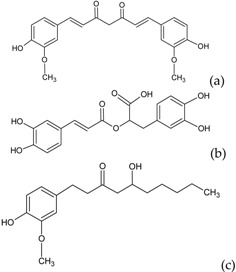 |
Curcumin (a) Rosmarinic acid (b) Gingerol (c) | Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) Ginger (Zingiber officinale) |
