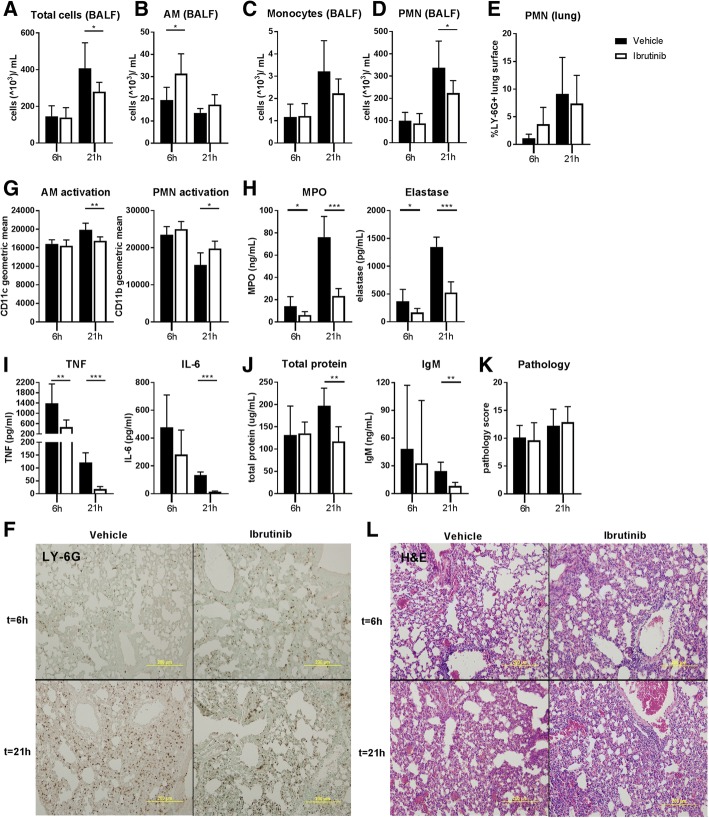
Fig. 2.
Ibrutinib reduces inflammatory myeloid cell responses during LTA-induced acute lung inflammation. Mice were treated with vehicle (n = 8) or ibrutinib (n = 8) via oral gavage and sacrificed 6 and 21 h after intranasal administration of lipoteichoic acid (LTA). Numbers of (a) total cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), (b) alveolar macrophages (AM), (c) monocytes and (d) polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) in BALF are depicted as 103cells/mL. (e) Percentage of LY-6G positive lung surface as a measure for total lung PMN numbers and (f) representative pictures of LY-6G staining. g CD11c expression (geometric mean) on BALF AM and CD11b expression (geometric mean) on BALF PMN. h Concentrations of PMN granular proteins myeloperoxidase (MPO) and elastase in BALF. i Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations in BALF. j Concentrations of total protein and immunoglobulin (Ig) M in BALF as a measure for plasma leakage into the lung. k Pathology score and l representative hematoxylin and eosin (h&e) pictures. Data are represented as mean and SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney U-test). Data represent results from a single experiment