Figure 2. NHA2 promotes cyst development in vitro .
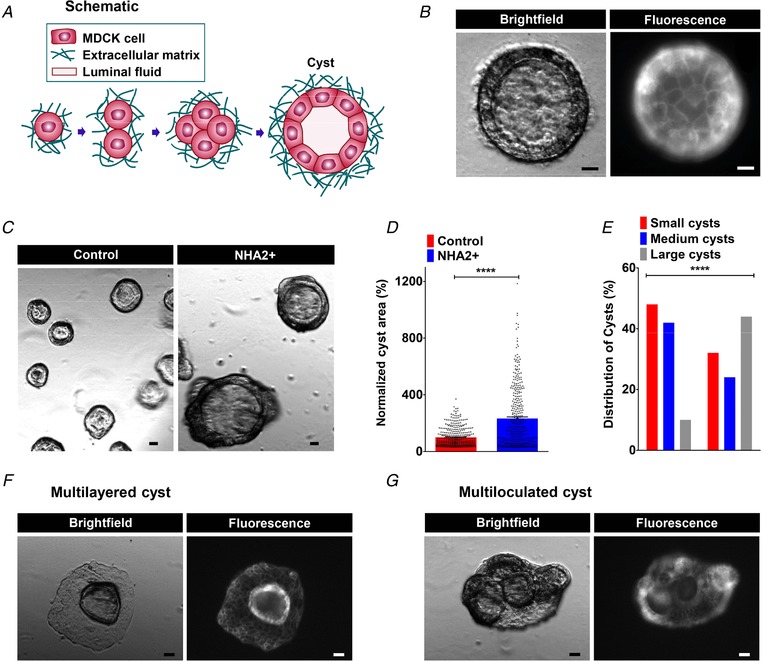
A, schematic depiction of in vitro MDCK cell model of cystogenesis in extracellular matrix (Matrigel). B, representative image of a MDCK cyst with polarized, single‐layer, thinned epithelium surrounding a fluid‐filled lumen (left; brightfield) with surface expression of NHA2–GFP (right; fluorescence). C, NHA2+ MDCK cells formed larger cysts (right) relative to control (left). D, quantification of cyst size on day 10 of culture showed significant cyst expansion from NHA2+ cells relative to control (Control: 100 ± 66.4, n = 363; NHA2+: 232.3 ± 213.7, n = 367; Student's t test, **** P < 0.0001). E, percentage of large cysts is significantly higher from NHA2+ cells as compared to control. Classification of cysts in three subclasses according to their relative diameter (small/medium/large) showed significantly elevated percentage of cysts with large size in NHA2+ and reduced percentage of cysts with small and medium sizes (χ2 test, **** P < 0.0001). F and G, representative images of MDCK cysts documenting mutilayered and multiloculated cysts in NHA2+ MDCK cells (left; brightfield) with surface expression of NHA2–GFP (right; fluorescence) that was not seen in cysts derived from control MDCK cells. Scale bars: 10 μm. All error bars are S.E.
