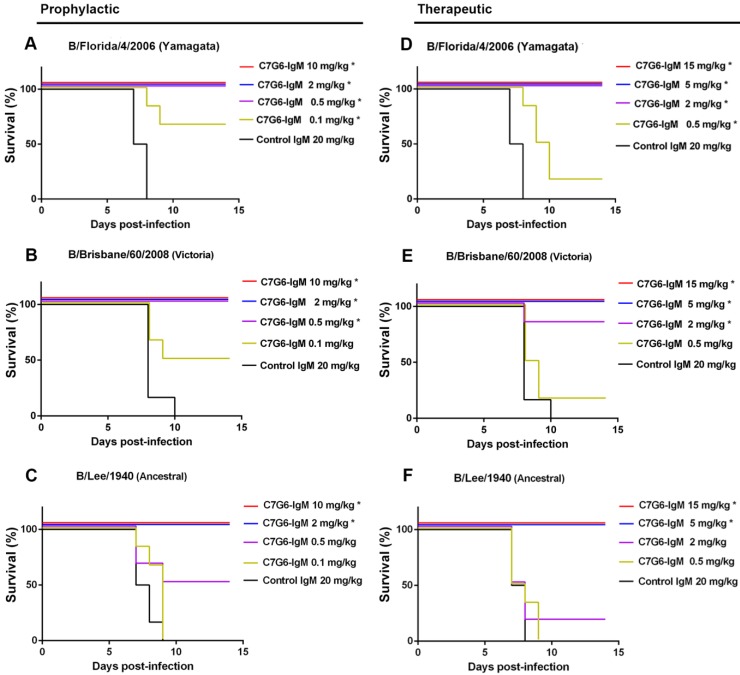
Figure 4.
In vivo prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of C7G6-IgM in mice. (A-C) Prophylactic efficacy of C7G6-IgM against lethal challenge with 25 MLD50 (50% mouse lethal dose) of MA-B/Florida/4/2006 (A), MA-B/Brisbane/60/2008 (B), or MA-B/Lee/1940 virus (C). The survival curves of BALB/c mice (n = 6 per group) treated with C7G6-IgM (10, 2, 0.5, or 0.1 mg/kg) or control IgM (20 mg/kg) 1 day before lethal challenge are shown. (D-F) For the therapeutic groups, survival curves for BALB/c mice (n = 6 per group) that received C7G6-IgM (15, 5, 2 or 0.5 mg/kg) or control IgM (20 mg/kg) 1 day after lethal challenge with 25 MLD50 of MA-B/Florida/4/2006 (D), MA-B/Brisbane/60/2008 (E), or MA-B/Lee/1940 (F) virus are shown. This experiment was repeated three times; one representative dataset is shown. The log-rank test was used to assess the significance (*P < 0.05) of survival outcome. The control IgM is C5G6-IgM (a mAb against the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus).