Figure 9. Exendin‐4 acutely mediates gap junction coupling via PKA in mouse islets.
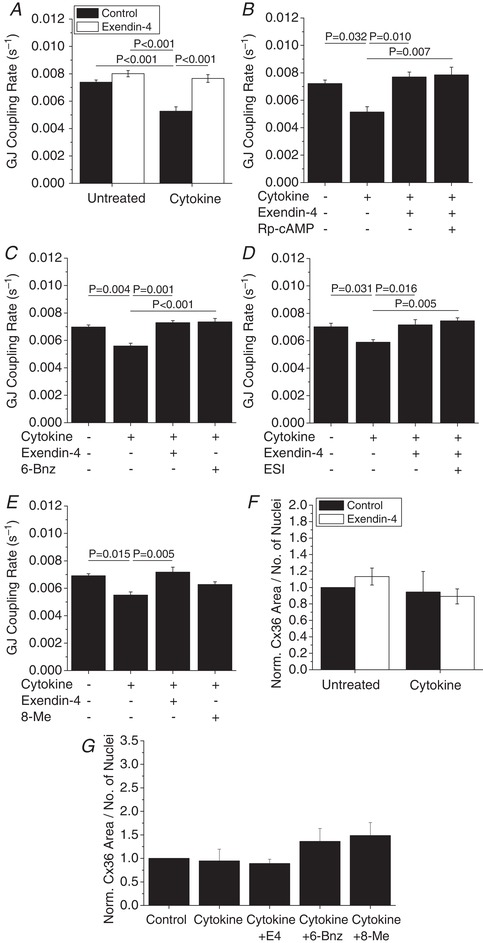
A–E, gap junction coupling (GJ coupling rate) based on fluorescence recovery rate (s−1) in mouse islets treated with cytokines and 10 nM exendin‐4 (n = 4–5) (A–E), 100 μM of the PKA inhibitor Rp‐cAMP (n = 4) (B), 300 μM of the PKA activator 6‐Bnz (n = 4) (C), 10 μM of the EPAC inhibitor ESI (n = 4) (D), or 300 μM of the EPAC activator 8‐Me (n = 4) (E) as indicated for 1 h. Data represent means ± SEM. P < 0.05 indicates a significant difference based on repeated measures ANOVA. F, quantification of Cx36 plaque area per number of nuclei in mouse islets treated with cytokines and 10 nM exendin‐4 as indicated for 1 h, normalized to control islets from each experiment (n = 3). G, quantification of Cx36 plaque area per number of nuclei in mouse islets treated with cytokines, 10 nM exendin‐4, the PKA activator 6‐Bnz, or the Epac2 activator 8‐Me as indicated for 1 h, normalized to control islets from each experiment (n = 3). Data represent means ± SEM. *Significant difference from control islets determined with 95% confidence intervals.
