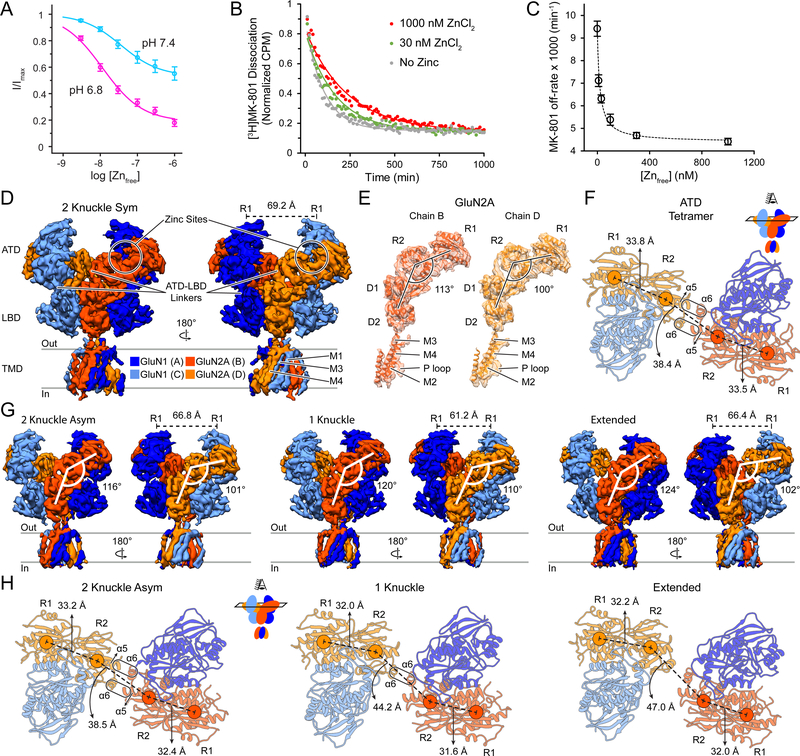
Figure 1. GluN1/GluN2A Diheteromeric Receptor Activity Modulation by Proton and Zinc, and CryoEM Structures at pH 7.4 in the Absence or Presence of 1 μM Zinc.
(A) Zinc-inhibition of the GluN1/GluN2A receptor construct at pH 7.4 (cyan, IC50 = 36 ± 1 nM) and pH 6.8 (magenta, IC50 = 12 ± 1 nM) in the presence of 100 μM glutamate and glycine. Imax is obtained by measuring currents in the absence of zinc. Data are mean ± SEM of 3–4 oocytes. See also Figure S1A-B.
(B) Dissociation of [3H]MK-801 from agonist-bound affinity-purified diNMDAR (100 μM glutamate and glycine) in the absence of zinc (grey), in the presence of 30 nM zinc (green), or 1 μM zinc (red). A single-exponential curve (solid lines) is used to obtain the off-rate of MK-801.
(C) Off-rate of [3H]MK-801 as a function of zinc at pH 7.4 in the presence of 100 μM glutamate and glycine. Zinc-inhibition IC50 = 17.3 ± 1.4 nM based on a one-site binding model. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent replicates.
(D and G) Side views of the diNMDAR cryoEM map in the presence of 1 mM glutamate and glycine at pH 7.4 with 1 mM EDTA (D) or in the presence of 1 μM zinc (G). The distance between the center of mass (COM) of the upper lobes (R1) of GluN1 ATD are shown. See also Figures S2–S4.
(E) Atomic model of each GluN2A subunit fitted into the density map. The ATD-LBD angle is indicated for the two subunits.
(F and H) Top view of the atomic model for the ATD of the diNMDAR in the absence of zinc (F) or in the presence of 1 μM zinc (H). COMs of R1 and R2 lobes for the two GluN2A subunits are shown (circles), with their distance indicated. The rounded rectangles represent the ‘knuckles’ and show the interaction between the α5 and α6 helices of opposing GluN2A subunits for the 2-knuckle conformations, and between α6 and α6 helices for the 1-knuckle conformation.