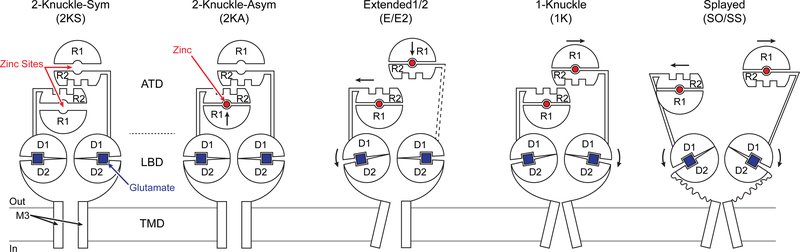
Figure 7. Schematic Summary for Zinc and Proton-Inhibition of GluN2A Containing NMDARs.
The schematics for the conformational changes in GluN2A subunits which lead from high PO conformations (2KS/2KA) to lower PO states (E-E2) and finally to states with PO close to zero (1K/SO/SS). These changes originate from the closure of both ATD clamshells in the presence of zinc and protons, leading to the rocking of the LBD clamshells, bringing the lower LBD lobes closer together, and releasing the tension on the gate. In the extended or extended-2 conformations, where one ATD heterodimer has lost interaction with the rest of the receptor, zinc and proton inhibition is not transduced efficiently through the LBD, leading to higher PO as compared to the 1knuckle state.