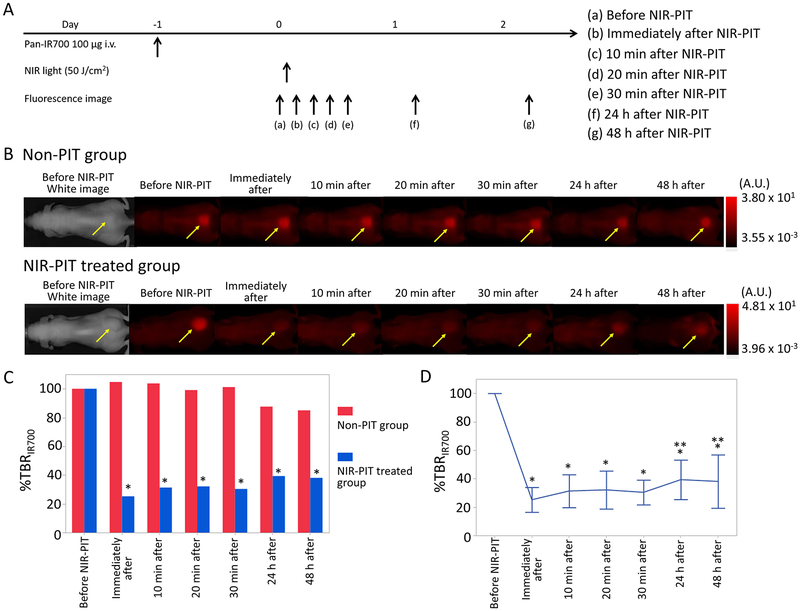
Figure 2.
IR700 fluorescence imaging in response to NIR-PIT. (A) NIR-PIT outline. IR700 fluorescence images were scanned at each time point as shown. (B) IR700 fluorescence real-time images of A431-luc-GFP tumor bearing mice for NIR-PIT. Yellow arrows indicate the tumor. IR700 fluorescence intensity greatly decreased in the early phase (0, 10, 20, 30 min later) after NIR-PIT. IR700 fluorescence intensities in the late phase (24 and 48 h later) after NIR-PIT were higher than those immediately after NIR-PIT. (C) Comparison of IR700 fluorescence intensity in A431-luc-GFP tumor bearing mice between non-PIT and NIR-PIT treated groups. %TBRIR700 in NIR-PIT treated group showed significant decreases at each time point after NIR-PIT compared with that in non-PIT group (*p < 0.05, vs non-PIT group, Mann–Whitney U-test). (D) Time course analysis of IR700 fluorescence intensity in the NIR-PIT treated group. %TBRIR700 at each time point after NIR-PIT showed significant decreases in comparison with pretreatment %TBRIR700 (*p < 0.05, vs pretreatment %TBRIR700, paired t-test). %TBRIR700 24 and 48 h after PIT showed significant increases in comparison with %TBRIR700 immediately after NIR-PIT (**p < 0.05, vs %TBRIR700 immediately after NIR-PIT, paired t-test).