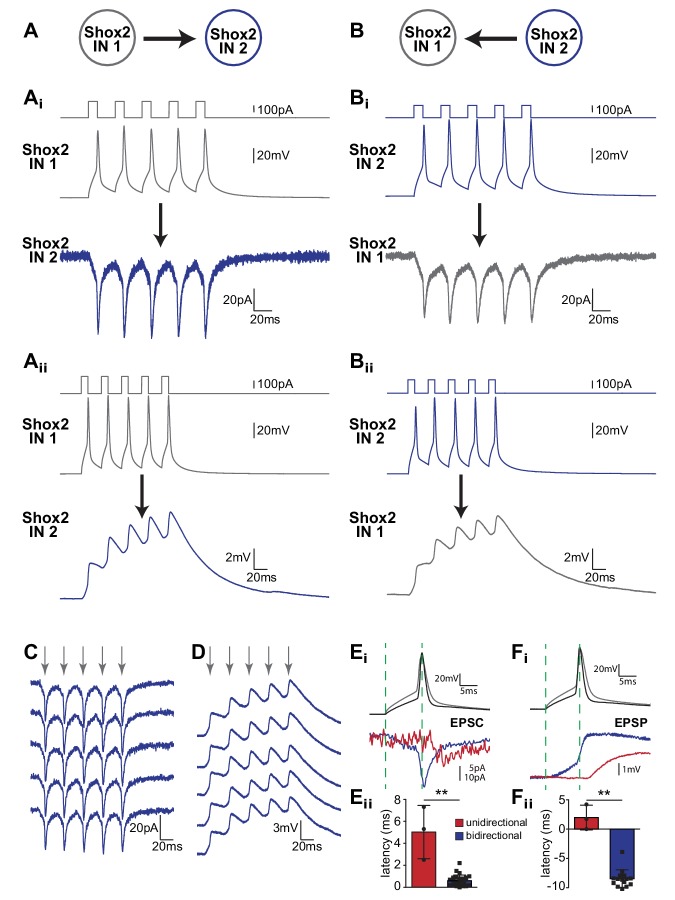
Figure 2. Bidirectional connections are present between Shox2 INs in neonatal spinal cord.
(A and B) Examples of recordings from a pair of bidirectionally connected Shox2 INs. (Ai and Bi) Cartoon corresponding to colors of traces in (A and B). (Ai and Aii) Current injections into Shox2 IN 1 evoked five action potentials (gray). Excitatory postsynaptic currents (Ai) or potentials (Aii) resulted in Shox2 IN 2 (blue) in voltage clamp or current clamp mode. Reversal of the protocol, current injection in Shox2 IN 2 (blue) also resulted in excitatory currents (Bi) or potentials (Bii) in Shox2 IN 1. All data in A and B were averages of 50 trials. (C and D) Examples of individual trials between bidirectionally connected pairs recorded in voltage clamp (C) and current clamp (D). Gray arrows signify the peaks of the presynaptic action potentials. Note the lack of failures and that responses appear nearly identical in each sweep. (Ei) Action potentials evoked in presynaptic unidirectionally (black) and bidirectionally (gray) connected pairs and examples of single postsynaptic currents (red, unidirectional; blue, bidirectional). Dotted lines highlight the beginning of the depolarization and action potential peak in the presynaptic cells, in order to visualize latency differences in the postsynaptic cells. (Eii) Mean latency of the EPSC peak, referenced to the peak of the evoked action potential between unidirectionally connected pairs (red) and bidirectionally connected pairs (blue). (Fi) Similar to Ei but current clamp recordings showing single EPSPs in postsynaptic unidirectional (red) and bidirectional (blue) Shox2 IN pairs in relation to the action potentials in their respective presynaptic Shox2 INs (black and gray). Dotted lines correspond to the start of the depolarization and the peak of the action potential in the presynaptic neurons to highlight the differences in the latency between the two types of connections. (Fii) Mean EPSP latency, peak of presynaptic action potential to start of postsynaptic depolarization, is shown for the unidirectional (red) and bidirectional (blue) Shox2 IN pairs. The depolarization in bidirectional pairs precedes the presynaptic action potential, resulting in a negative latency value. ** indicates p<0.01. Error bars represent SD.