Figure 3.
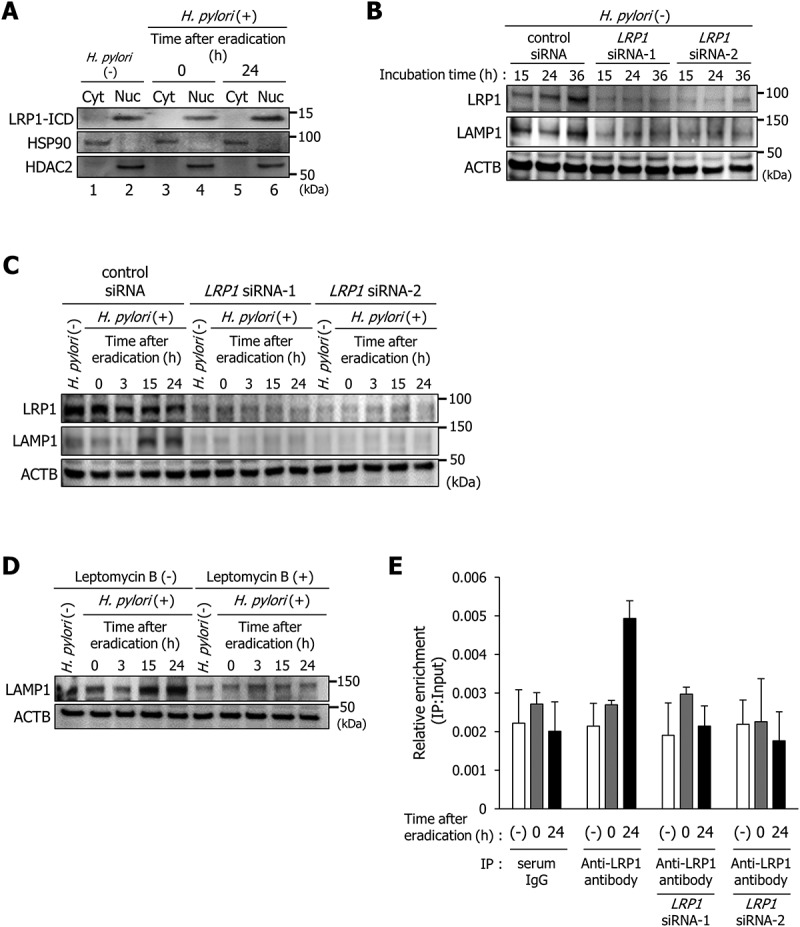
LRP1-ICD induces LAMP1 expression via binding to the LAMP1 proximal promoter. (a) AGS cells were infected with H. pylori for 5 h (MOI 50) and incubated in a medium containing antibiotic for 0 and 24 h. Then, subcellular fractionation of these cells indicated the localization of LRP1-ICD in cytoplasmic (Cyt) and nuclear (Nuc) extracts. (b) AGS cells were transfected with control, LRP1 siRNA-1, or LRP1 siRNA-2, and incubated for the indicated time period prior to analysis of protein extracts with the indicated antibodies by western blot. (c) AGS cells were transfected with control, LRP1 siRNA-1, or LRP1 siRNA-2, infected with H. pylori for 5 h (MOI 50), and incubated in a medium containing antibiotic for the indicated times, then analyzed by western blot. (d) AGS cells were treated with 200 nM leptomycin B, infected with H. pylori for 5 h (MOI 50), and incubated in a medium containing antibiotic for the indicated times. (e) AGS cells were transfected with LRP1 siRNA-1 or LRP1 siRNA-2, infected with H. pylori for 5 h (MOI 50), incubated in a medium containing antibiotic for 0 or 24 h, and then a ChIP assay was performed on these cells by using an anti-LRP1-carboxyterminal end antibody or an IgG from rabbit serum. Real-time PCR demonstrated relative enrichment of LAMP1 target promoter genes in the DNA fragments pulled down by an anti-LRP1-carboxyterminal end antibody and an IgG from rabbit serum. The result shown is representative of those observed in 2 independent experiments.
