Figure 2. Estimates of AHT probability (with 95% CIs) for 72 observed combinations of the PediBIRN-7’s seven predictor variables, applying physicians’ final diagnoses to classify AHT vs. non-AHT.
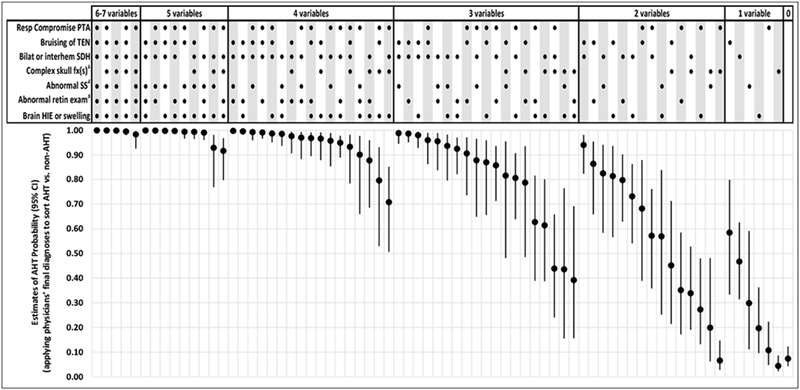
Abbreviations: AHT=abusive head trauma; CI-confidence interval; RESP=respiratory; PediBIRN=pediatric brain injury research network; PTA=priorto admission; TEN=torso, ear(s) or neck; SDH=subdural hemorrhage or fluid collection(s); fx(s)=fracture(s); HIE=hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
1Defined a priori as any skull fracture(s) other than an isolated, unilateral, nondiastatic, linear, parietal skull fracture
2Defined a priori as skeletal survey that reveals rib fracture(s), classic metaphyseal lesion fracture(s), epiphyseal separation(s), fracture(s) of the scapula or sternum, fracture(s) of digit(s), vertebral body fracture(s) or dislocation(s), OR fracture(s) of spinous process(es)
3Defined a priori as retinal exam by an ophthalmologist that reveals retinoschisis OR retinal hemorrhages described as dense, extensive, covering a large surface area, and/or extending to the ora serrate
[NOTE: Clinicians should not use these probability estimates when applying the PediBIRN-4, as doing so would be to assume that skeletal survey and retinal exam are normal.]
