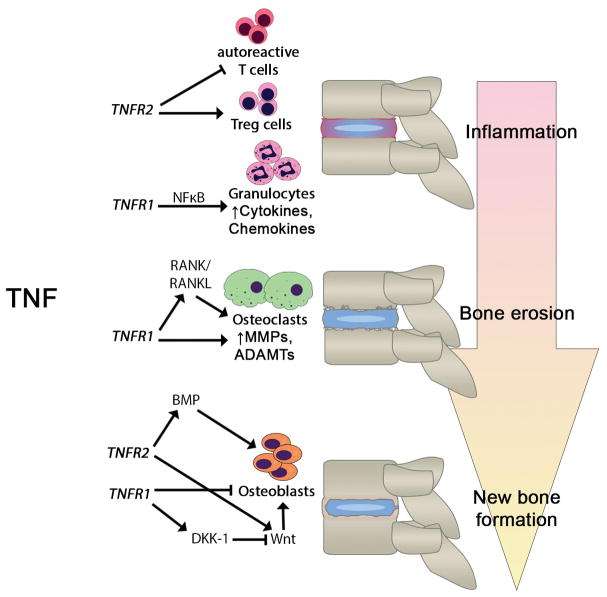
Figure 1.
The role of TNF in the progression of ankylosing spondylitis. This figure illustrates the opposing roles of two TNF receptors, TNFR1 and TNFR2, in inflammation, bone erosion, and new bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis. In general, TNFR1 is pro-inflammatory and mediates tissue catabolism, whereas TNFR2 is anti-inflammatory and mediates tissue anabolism. The pathways and molecular mediators involved are indicated. Abbreviations: ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; DKK-1, dickkopf-related protein-1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-B, RANK/RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B/RANK ligand; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor.