FIGURE 5.
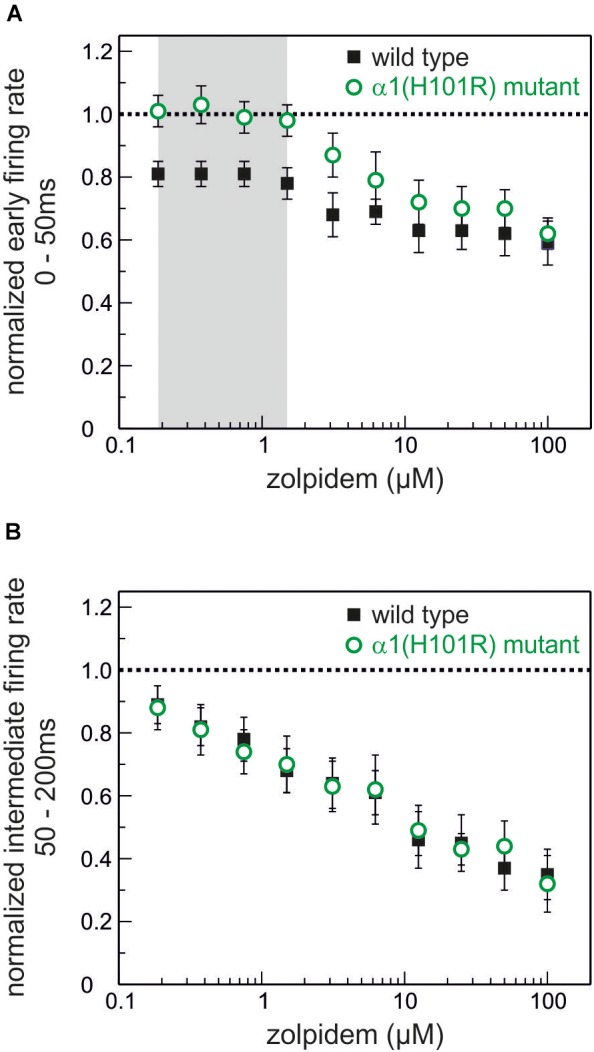
Actions of the α1-GABAA receptor-preferring drug zolpidem on neuronal activity. (A) Effects of zolpidem (concentration range 188 nM – 100 μM) on the normalized action potential rate during phases of high neuronal activity (0 – 50 ms after the beginning of an up state) in wild type (black) and GABAA α1(H101R) (green) cultured cortical neurons. The network-depressant action of zolpidem at low concentrations (up to 1.5 μM, marked in gray) is absent in neurons from GABAA α1(H101R) mice. Starting at a concentration of 3.125 μM inhibition of action potential firing during phases of high neuronal activity can be observed in GABAA α1(H101R) neurons and at higher concentrations runs parallel to the effects in wild type neurons (mean ± SEM, n = 22 – 46 for wild type and 8 – 38 for α1(H101R) mutant). (B) Effects of zolpidem on intermediate neuronal activity (during the time window of 50 – 200 ms after the beginning of an up state). Zolpidem depresses neuronal activity in a concentration-dependent manner in both wild type (black) and GABAA α1(H101R) (green) cortical neurons (mean ± SEM, n = 16 – 41 for wild type and 12 – 34 for α1(H101R) mutant). Unlike in A (high neuronal activity 0 – 50 ms after up state initiation) there is no difference between the action of zolpidem in wild type and GABAA α1(H101R) neurons. Data is displayed as mean ± SEM.
