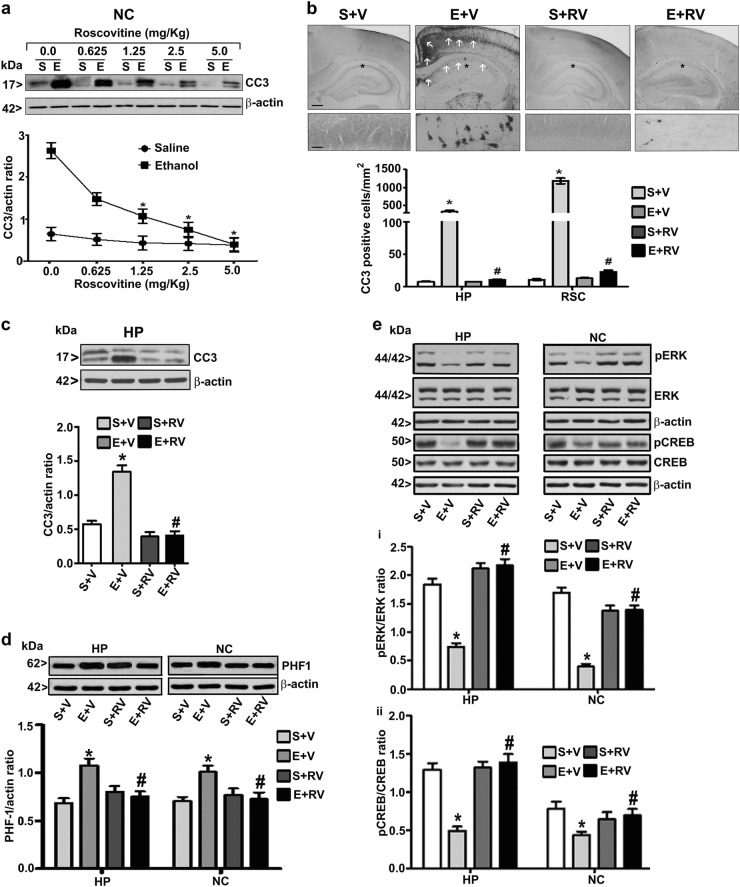
Fig. 2.
Pharmacological inhibition of CDK5/p25 activity with roscovitine (RV) dose-dependently prevents the accumulation of cleaved caspase-3 (CC3), phosphorylated tau (PHF1), and impaired pERK1/2 and pCREB caused by ethanol exposure in P7 mice. Mice were exposed to a high dose of ethanol after preadministration (30 min) with various doses of RV (0–5 mg/kg) or vehicle, and CC3 levels were determined in NC brain samples by a western blot analysis (a). Saline and 8 h ethanol-exposed mice were pretreated with 2.5 mg/kg RV for 30 min, the free-floating coronal brain sections (HP and retrosplenial cortex (RSC)) were subjected to IHC analysis with anti-rabbit-CC3 and CC3-positive cells were counted in the HP and RSC brain regions. The arrows indicate the CC3-positive neurons in the HP and RSC. Scale bars = 200 μm (b). The hippocampal region was enlarged to show the CC3-positive cells (asterisk (*)). CC3 levels were also determined in HP brain region by a western blot analysis (c). The HP and NC tissue fractions were subjected to western blot analysis with specific PHF1 (d), pERK1/2, ERK1/2 (e, i), and CREB and pCREB (e, ii) antibodies. The protein samples were equally loaded, confirmed with Ponceau S staining, and normalized to total proteins (ERK1/2 and CREB) followed by β-actin. (*p < 0.05 vs. S; #p < 0.05 vs. E). Error bars, SEM (n = 8 pups/group)