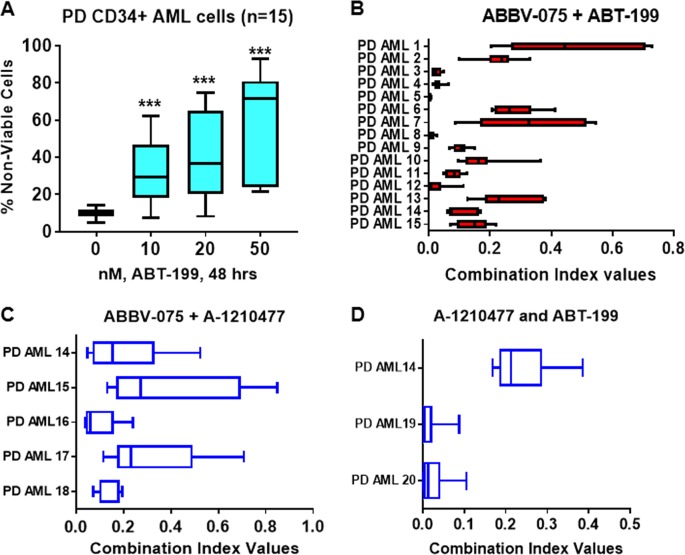
Fig. 5. Cotreatment with ABBV-075 and ABT-199 or MCL1 inhibitor exerts synergistic lethal activity against patient-derived (PD) AML BPCs.
a PD, CD34+ AML BPCs were treated with the indicated concentrations of ABT-199 for 48 h. At the end of treatment, cells were stained with To-Pro-3 iodide and the % of nonviable cells were determined by flow cytometry. A box plot was generated utilizing GraphPad V7. *** = p < 0.005 compared to the untreated control cells. b PD, CD34+ AML BPCs (n = 15) were treated with ABBV-075 (dose range: 20–250 nM) and ABT-199 (dose range: 10–100 nM) for 48 h. Following this, the % of nonviable cells was determined by flow cytometry. Combination index values were calculated by Compusyn and graphed utilizing GraphPad V7. c PD, CD34+ AML BPCs (n = 5) were treated with ABBV-075 (dose range: 20–250 nM) and A-1210477 (dose range: 1–10 µM) for 48 h. Following this, the % of nonviable cells was determined by flow cytometry. Combination index values were calculated by Compusyn and graphed utilizing GraphPad V7. d PD CD34+ AML BPCs (n = 3) were treated with A-1210477 (dose range: 2–10 µM) and ABT-199 (dose range: 10–50 nM) for 48 h. Following this, the % of nonviable cells was determined by flow cytometry. Combination index values were calculated by Compusyn and graphed utilizing GraphPad V7. BPC blast progenitor cell