Figure 7.
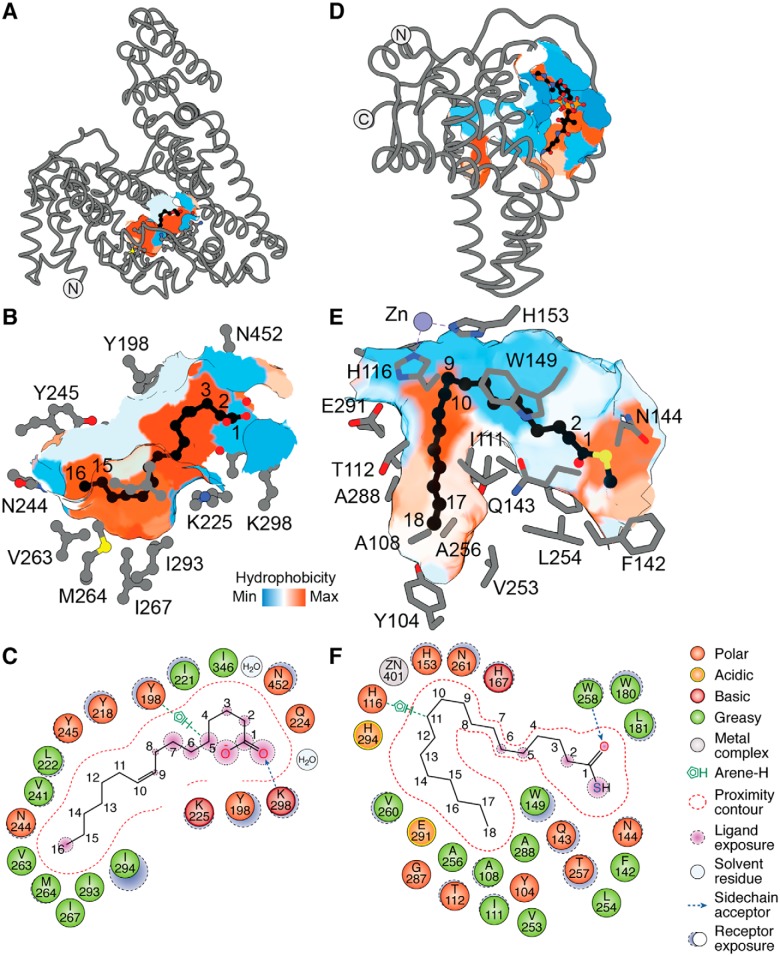
Fatty acid-binding proteins utilize diverse cavities with specific geometry to accommodate their ligands. A, structure of affamin in complex with C16:1n-7 fatty acid bound at its hydrophobic groove (surface representation), with B, a zoomed-in view highlighting side chains of residues within ∼5 Å distance from the fatty acid (PDB code 5OKL). C, ligand interaction map of C16:1n-7 in complex with affamin. D, structure of mSCD1 in complex with CoA–C18:0 occupying its hydrophobic cavity, with E, a zoomed-in view highlighting side chains of residues within ∼5 Å distance from the bound lipid chain (PDB code 4YMK). F, ligand interaction map of the fatty acyl moiety of the C18:0–CoA. The CoA moiety was hidden for clarity to highlight the acyl chain. Artwork by Luciana Giono.