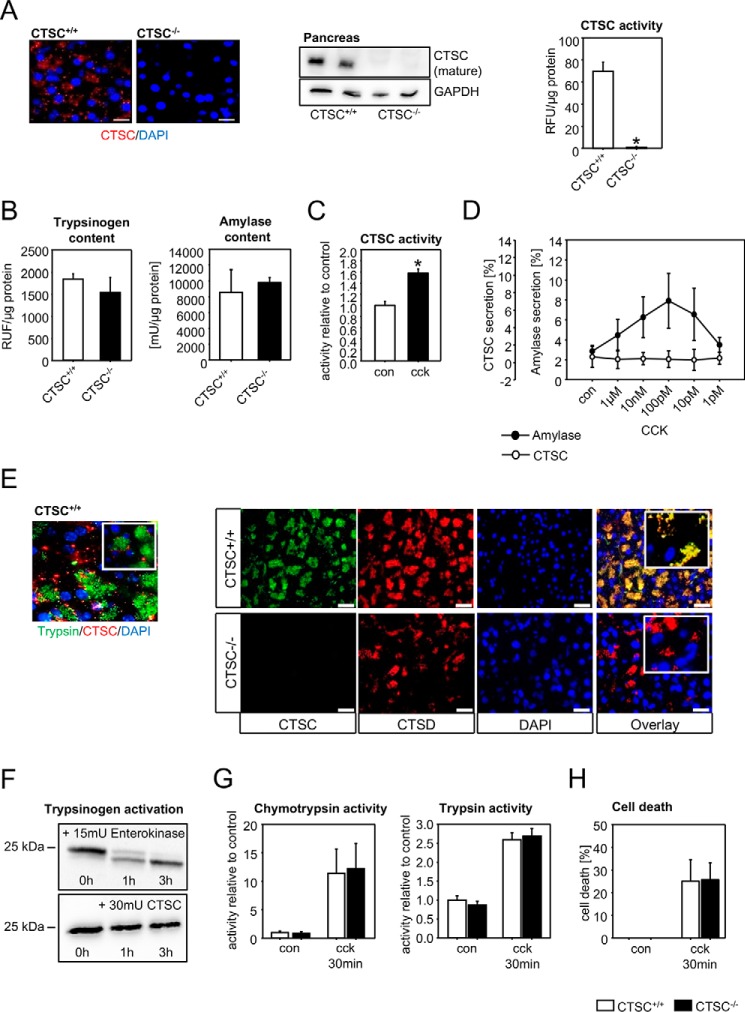
Figure 1.
Cathepsin C is expressed in the pancreas, activated in pancreatitis, but not involved in intra-acinar cell protease activation. A, cathepsin C is expressed in pancreatic exocrine tissue but is absent in CTSC−/− mice, as shown by antibody labeling and immunofluorescence staining, Western blotting from pancreas homogenates, and enzyme activity in acinar cells. B, trypsinogen content and amylase content are identical in CTSC−/− mice and controls. C, CTSC is intracellularly activated in isolated acinar cells upon supramaximal CCK stimulation. D, CTSC, unlike amylase, is not secreted from acinar cells. E, CTSC only marginally co-localizes with the zymogen marker trypsin but mainly co-localizes with the lysosomal protein CTSD in pancreatic acinar cells shown by immunofluorescence. F, CTSC, unlike enterokinase, does not directly activate trypsinogen in vitro. G, ex vivo activation of chymotrypsinogen and trypsinogen in CTSC−/− acinar cells upon supramaximal CCK concentrations does not differ from WT acini. H, cell death, measured as propidium iodide exclusion, was not different in CTSC−/− or WT acini. At least five animals were used for each experiment, and all experiments were performed in triplicate. All experiments were performed independently three or more times. The values represent means ± S.E. *, p < 0.05. Scale bar, 50 μm. con, control; DAPI, 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole; RFU, relative fluorescence units; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.