Figure 2.
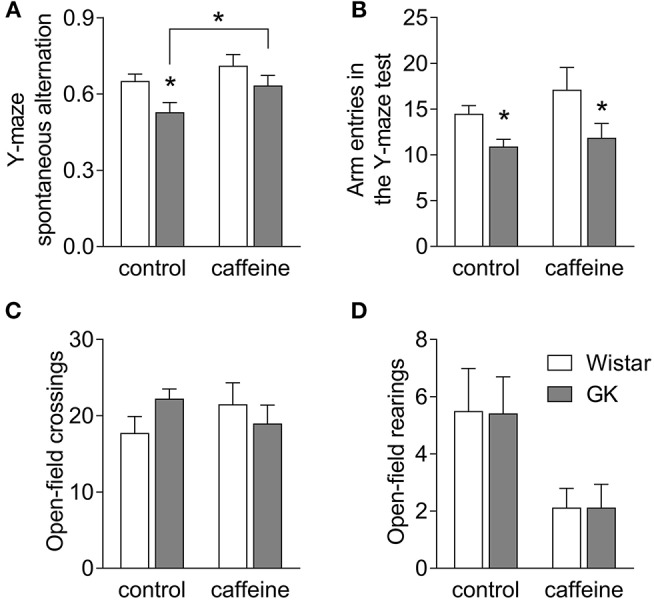
Caffeine consumption improves spatial working memory deficits in diabetic GK rats. GK rats displayed reduced spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze, when compared to controls, but not if treated with caffeine for 4 months (A). The number of entries in the Y-maze arms was lower in GK compared to control rats irrespective of caffeine consumption (B). The number of crossings in the open-field arena was unaltered by diabetes or caffeine consumption (C), but the number of rearing events was reduced upon chronic caffeine consumption (D). Data are mean ± SEM of 8 rats per group. Symbols represent LSD test results after ANOVA with either significant diabetes effect or significant diabetes-caffeine interaction: *P < 0.05 for GK vs. Wistar in the respective treatment group or as indicated.
