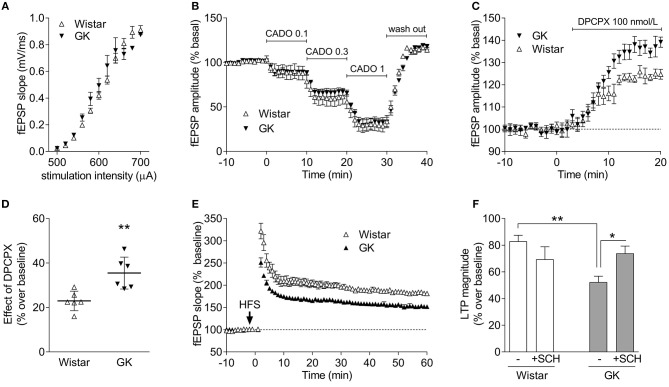
Figure 7.
GK rats display an unchanged A1R-mediated inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus but an increased A2AR-mediated control of synaptic plasticity. (A) Superimposed input-output curves in GK (filed symbols) and Wistar rats (open symbols), indicating a similar density of excitatory innervation in Schaffer fiber-CA1 pyramid synapses of hippocampal slices. (B) Superimposable concentration-dependent curves of inhibition of CA1 hippocampal field excitatory post-synaptic potentials (fEPSPs) by the closest chemical analog of adenosine, 2-chloroadenosine (CADO; applied at concentrations of 0.1, 0.3, and 1 μmol/L), showing that the A1R-mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission is similar in GK and Wistar rats. The fEPSP slope before CADO application is normalized to 100%, and 0% corresponds to a complete inhibition of fEPSPs. (C,D) GK rats seem to have higher levels of endogenous extracellular adenosine tonically activating inhibitory A1R, as revealed by the larger disinhibition of fEPSPs by the selective A1R antagonist, DPCPX. (E) Averaged time course changes of fEPSP slope induced by a high-frequency stimulation train (HFS 100 Hz, 1 s, applied when indicated by the arrow) in hippocampal slices taken from Wistar (open symbols) or GK rats (filed symbols), showing that the amplitude of LTP is larger in Wistar than in GK rats. (F) The presence of the A2AR antagonist SCH58261 (50 nM, +SHC), which was applied 30 min before LTP induction and remained in the bath up to the end of the experiment, has a discrete effect in Wistar rats (open bars) and efficiently restores LTP amplitude back to control levels in GK rats (gray bars). The electrophysiological data are mean ± SEM of 5–6 animals per experimental condition. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 using either an unpaired Student's t test in (C) or a two-way ANOVA followed by a LSD post-hoc test in (F).