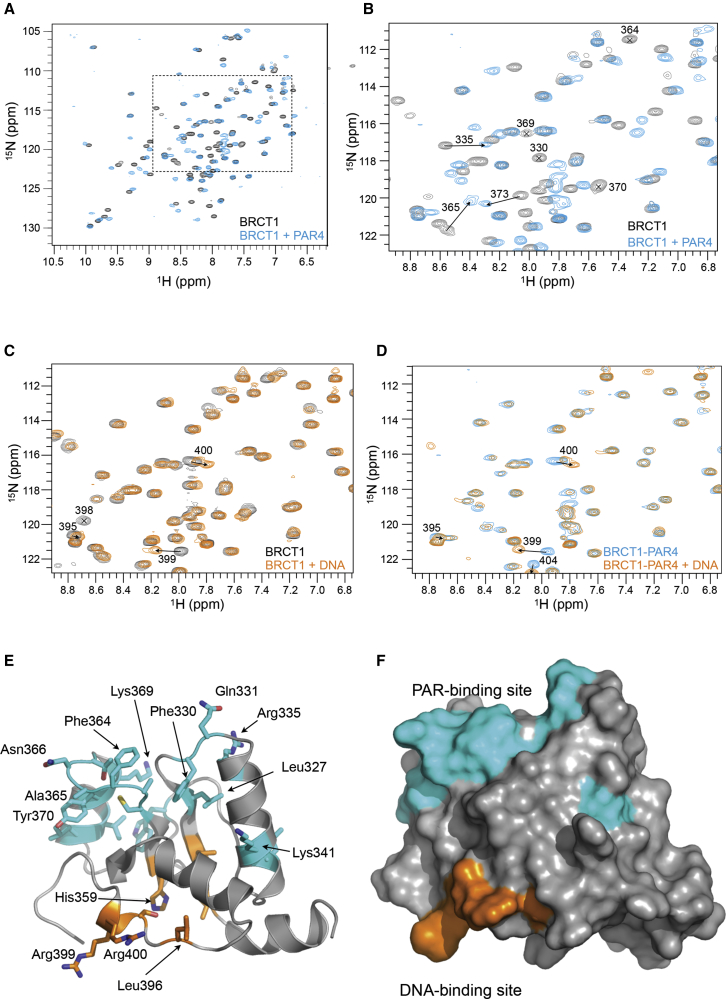
Figure 2.
Mapping PAR- and DNA-Binding Sites
(A) 1H–15N heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) NMR spectra for XRCC1-BRCT1 alone (black) overlayed with the HSQC spectrum for XRCC1-BRCT1 in the presence of a fragment of poly(ADP-ribose)—PAR4 (cyan; see STAR Methods). Assignments for these and other spectra have been deposited in the Biological Magnetic Resonance Bank (BRMB: 27598).
(B) Close up of boxed region in (A), highlighting residues in and around the putative phosphate-binding pocket in XRCC1-BRCT1, whose chemical shift changes on binding of PAR4.
(C) Close up of equivalent region to (B), showing the HSQC spectra for XRCC1-BRCT1 alone (black), overlayed with the HSQC spectrum for XRCC1-BRCT1 in the presence of a 19-mer dsDNA with a 5′-phosphorylated nick on one strand, 8 nucleotides in from the 3′ end (orange)—see Figure S1. Residues whose chemical shifts change on binding of the dsDNA are highlighted.
(D) As (C) but showing the overlay of HSQC spectra for XRCC1-BRCT1 bound to PAR4 (cyan) with that of XRCC1-BRCT1 + PAR4 with the addition of nicked, 5′-phosphorylated dsDNA (orange). Residues that display a change in chemical shift on binding of dsDNA to XRCC1-BRCT1 alone display very similar shifts when the dsDNA is added to XRCC1-BRCT1 already bound to PAR4, showing that the binding sites for PAR4 and dsDNA are non-overlapping and that these two ligands are not mutually competitive.
(E) Secondary structure cartoon of the NMR structure of XRCC1-BRCT1 (PDB: 2D8M), with residues showing perturbed peptide backbone chemical shifts on PAR4 binding highlighted in cyan and those whose chemical shifts are perturbed by binding of nicked dsDNA, highlighted in orange. Highlighted residues are those whose chemical shift perturbation exceeds 2 SD of the average chemical shift across the whole domain or those where the peak becomes broadened.
(F) As (E) but with a solvent-accessible surface representation showing the non-overlapping binding sites for PAR and for dsDNA on opposite faces of the domain.