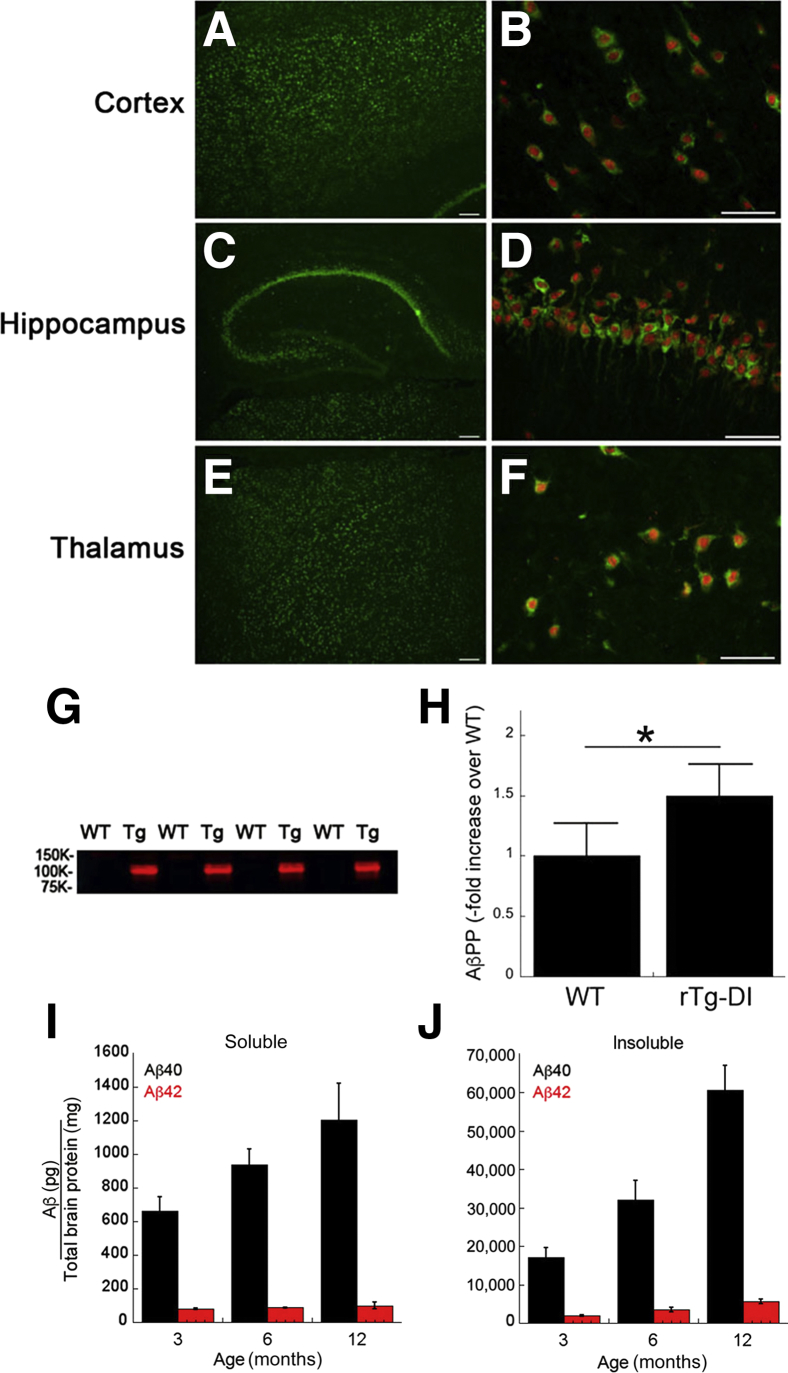
Figure 1.
Analysis of transgenic human AβPP expression and progressive Aβ accumulation in rTg-DI rats. Brain sections from 2-month–old rTg-DI rats were immunolabeled with the mouse monoclonal antibody P2-1 to specifically detect human AβPP (green) and the rabbit polyclonal antibody NeuN to detect neurons (red). A–F: There was widespread human AβPP expression in neurons in the cortex (A and B), hippocampus (C and D), and thalamus (E and F). G: Immunoblot analysis of human AβPP expression in total brain homogenates from wild-type (WT) and rTg-DI (Tg) rats. H: Quantitative immunoblotting was performed to measure total AβPP (endogenous rat AβPP + transgenic human AβPP) in brain homogenates of wild-type and rTg-DI rats. The level of transgene human AβPP expression is approximately 50% the amount of endogenous rat AβPP. I and J: The levels of soluble (I) and insoluble (J) Aβ40 and Aβ42 peptides in the forebrain of progressively aged rats were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, as described in Materials and Methods. The data are of triplicate measurements. Data are expressed as means ± SD (H–J). n = 5 rats per group (H). n = 5 to 6 rTg-DI rats per group (I and J). ∗P < 0.05. Scale bars: 10 μm (A, C, and E); 50 μm (B, D, and F).