Figure 4.
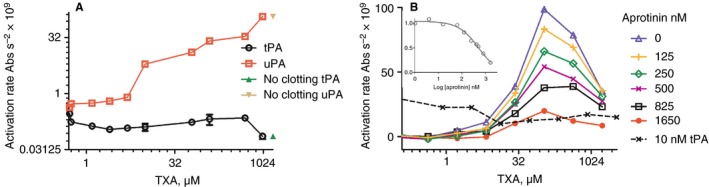
Generation of plasmin from clots incubated with urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) or tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and tranexamic acid (TXA). Panel A used the plasma clot halo system where plasminogen activator, TXA and plasmin chromogenic substrate S‐2251 were added to preformed clots. Initial rates of plasmin generation were calculated from plots of absorbance vs. time squared 22 and the points shown are means ± standard deviations (SDs) of duplicate wells. Panel B shows similar data for plasma clots in the microtiter plate format used in Fig. 1, with 5 nmol L−1 uPA incorporated into the clots (or 10 nmol L−1 tPA as shown). Chromogenic substrate S‐2251 containing a range of TXA and aprotinin as shown was added to preformed clots (all points show plasminogen activation rates from single wells). The insert shows inhibition of peak plasmin generation by increasing aprotinin concentrations, with IC50 = 530 ± 119 nmol L−1 (± standard error [SE] of fitting).
