Figure 6.
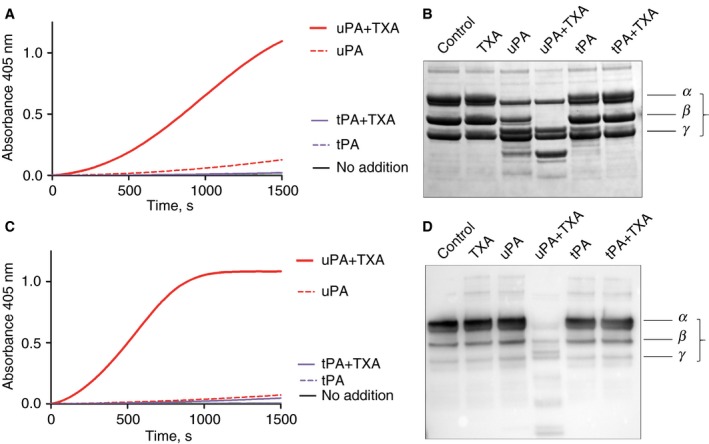
Digestion of fibrinogen by mixtures of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and tranexamic acid (TXA). Panels A and B show the effects of activator, 5 nmol L−1 uPA or 2.5 nmol L−1 tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) with or without the addition of 400 μmol L−1 TXA on fibrinogen in a purified system. Panel A is a trace showing absorbance changes from S‐2251 hydrolysis as a result of plasmin generation, from 200 nmol L−1 plasminogen with 1 mg mL−1 fibrinogen, in the presence of uPA + TXA, but not with tPA. The corresponding Coomassie stained SDS PAGE of reaction mixtures after 30 min illustrates that the generated plasmin is able to digest fibrinogen in the presence of TXA (the α, β, and γ chains of fibrinogen are annotated). Panels C and D replicate these results using V.I. plasma (with 0.4 U mL−1 of α2‐antiplasmin) under the same conditions used for Fig. 5(C). Plasmin was rapidly generated in the presence of 5 nmol L−1 uPA and 400 μmol L−1 TXA, as shown in panel C. This plasmin was able to substantially and rapidly destroy the normal level of 3.2 mg mL−1 fibrinogen present in this plasma sample, as shown by the western blot using anti‐fibrinogen antibodies in panel D.
