Figure 4.
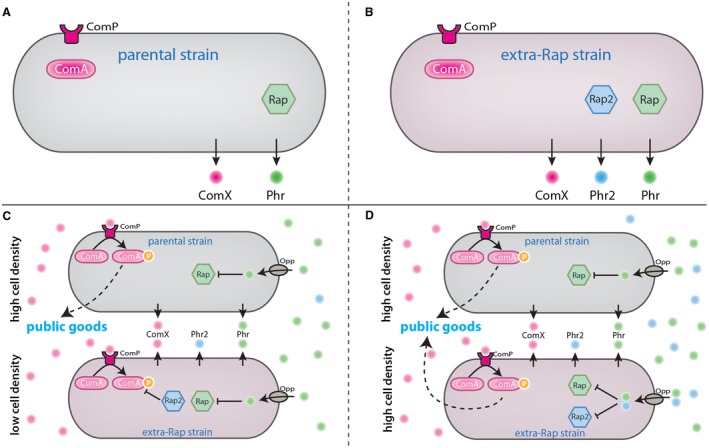
Quorum sensing and cheating. Schematic of the effect that acquisition of an additional Rap/Phr system has in Bacillus subtilis cheating. A. Representation of the parental strain, which encodes for the Com system and a single Rap/Phr system. The cell produces ComX pheromones and Phr peptides. B. The ‘Extra‐Rap’ strain, which has the same Com and Rap/Phr system as the parental strain plus an additional Rap/Phr (Rap2/Phr2, shown in blue) system. C. When the parental strain is at a quorum and the ‘Extra‐Rap’ strain is at a low density in the population, the extracellular concentrations of ComX and Phr are high, while Phr2 is present at low concentrations in the extracellular environment. ComX and Phr enter all cells (both the parental and ‘Extra‐Rap’). ComX leads to phosphorylation of ComA and Phr represses Rap. In the parental strain, ComA is free to facilitate public good production; while, in the ‘Extra‐Rap’ system, the absence of intracellular Phr2 results in a Rap2 repressing ComA~P, thereby repressing public good production. D. When both the parental strain and the ‘Extra‐Rap’ strain are at a quorum, public goods are produced by the parental strain as described in C). In the ‘Extra‐Rap’ strain, increased extracellular concentration of Phr2 results in the peptide entering the cell and repressing Rap2, allowing a contribution to public good production.
